Introduction
Introduction
The following MRI is from a 19 year old male who presented with syncope and the study was performed to identify a possible arrhythmogenic focus. It is a good exercise to help evaluate size
- Buzz
- Overall volume
- RV volume is <2/3 the volume of LV
- LA and RA are about 1/3 volume of the RV and LV
- Peak systole volume in LV and RV should = 1/3 of diastolic volume
- Shapes
- LA rectangular with flat back
- RA flat back
- LV Ovoid with icecream cone shaped cavity
- RV triangular shaped and septum bulges into it (“punch in the belly”
- Linear Size
- LA +/- 4cms (post wall to MV)
- LV +/- 5cms (transverse) not >6
- RV +/- 4cms (transverse) not >6
- RA +/- 5cms (post wall to TV)
- Wall thickness
- Measure in diastole
- LV 1.2 to 1.4cms
- RV 3-4mms
- Measure in diastole
- Overall volume
Normal 4 Chambered View
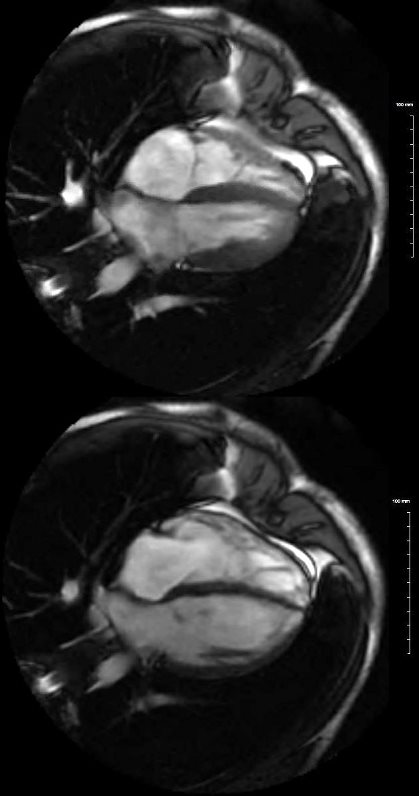
White blood imaging using 4 chamber view shows a normal sized heart in systole (above) and diastole below. The left and right atria have flattened surfaces, and occupy about 1/3 the volume of the ventricles. The RV volume is about 2/3 the volume of the LV. The wall of the LV in diastole (lower image) is less than 1 cms and the wall of the RV is barely seen and is in the range of about 3mm. Note in diastole the MV and TV are open
Ashley Davidoff MD

White blood imaging using 4 chamber view shows a normal sized heart in systole (above) and diastole (below). The left ad right atria have flattened surfaces, and occupy about 1/3 the volume of the ventricles. The A-P dimension of the LA during diastole is about 4cms (normal) and the RA is about 5cms (normal). The RV volume is about 2/3 the volume of the LV. The transverse dimension of the RV in diastole is about 4cms and the LV 5cms – both normal. The septum of the LV in diastole (lower image) is less than 9mm, and the free wall is 9mms (upper limits normal is 1.2 cms. The wall of the RV is barely seen and is in the range of about 3mm. Note in diastole the MV and TV are open. The difference in diameter of the RV in systole and diastole is about 2/3 and similarly of the LV. This an approximately normal ratio
Ashley Davidoff MD
Short Axis
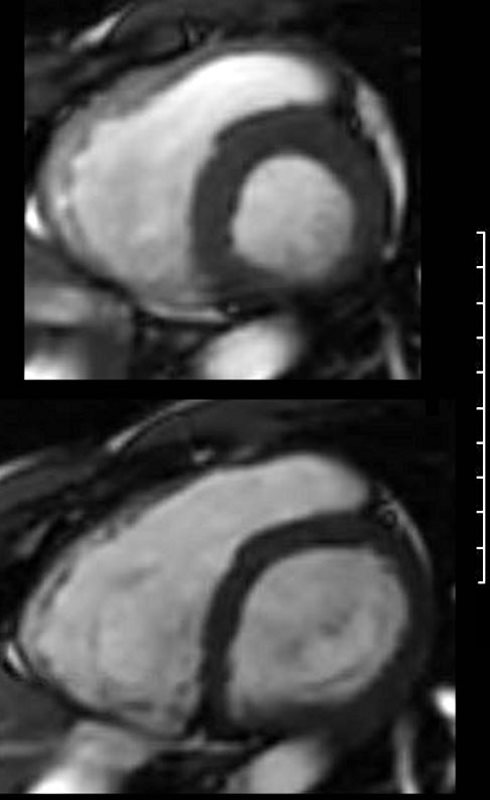
White blood imaging using short axis view shows a normal sized heart in systole (above) and diastole (below). The left and right ventricles show normal wall thicknesses and the volume of the chambers in systole are about 2/3 the volume in diastole (normal). There is no obvious dyskinetic segment of the RVOT.
Ashley Davidoff MD
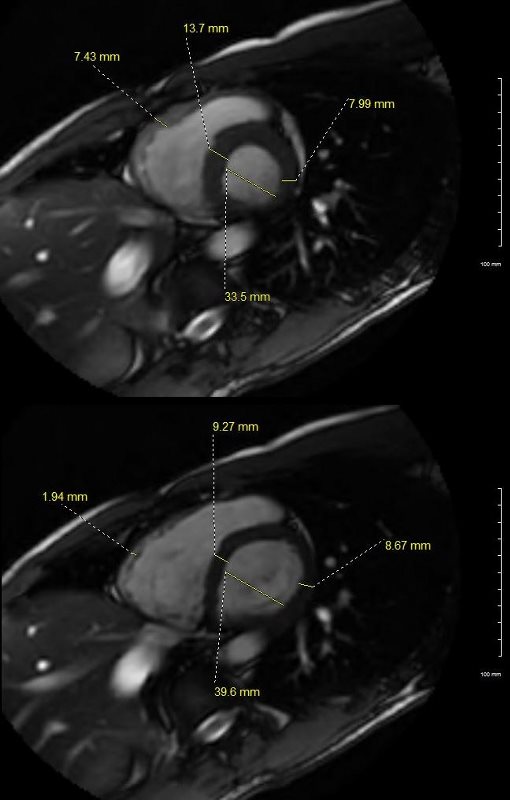
White blood imaging using short axis view shows a normal sized heart in systole (above) and diastole (below). The transverse dimension of the LV is 4cms in diastole which is normal. The septum of the LV in diastole (lower image) is less than 9.2mms, and the free wall is 8.7 mms (upper limits normal is 1.2cms). The wall of the RV is barely seen in diastole and measures about. In systole the residual volume of the RV is about 1/3 the diastolic volume indicating an approximate ejection of 2/3 = 66% ejection fraction (EF). Similarly, at peak LV systole the residual volume of the LV is about 1/3 the diastolic volume indicating an approximate ejection of 2/3 = 66% ejection fraction (EF).
Ashley Davidoff MD
3 Chamber View – LVOT
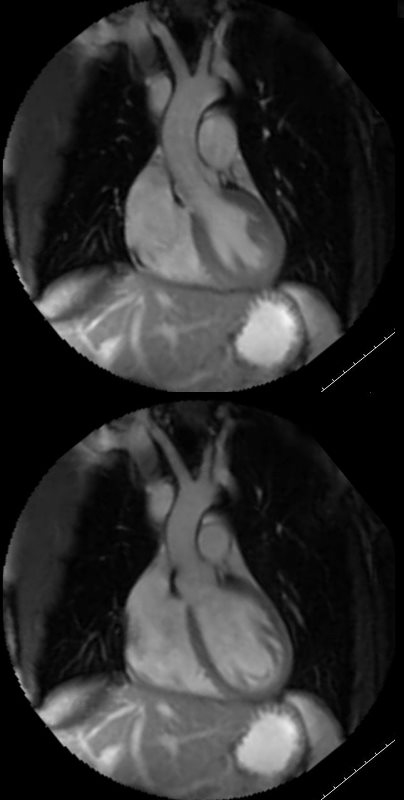
White blood imaging of the LVOT view shows a normal sized ovoid LV in systole (above) and diastole (below). The walls appear normal thickness in the diastolic image, and the approximate residual volume of the LV at peak systole is about 1/3 the diastolic volume indicating an approximate ejection of 2/3 = 66% ejection fraction (EF).
Ashley Davidoff MD
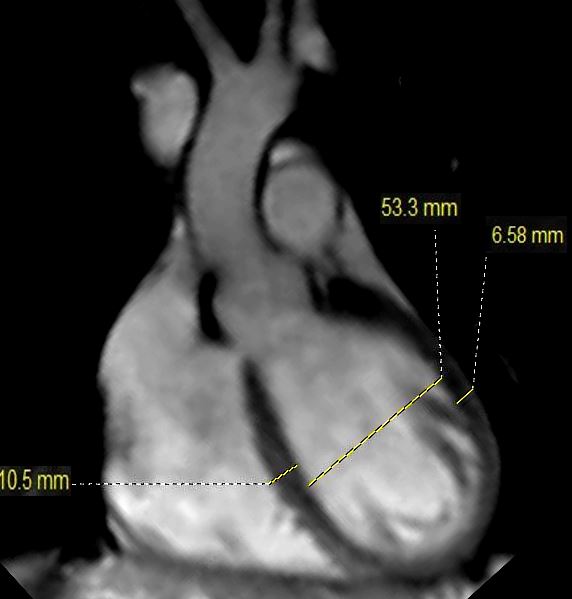
This is the MRI of a 19-year-old male who presented with syncope and the study was performed to identify a possible arrhythmogenic focus
White blood imaging of the LVOT view shows a normal sized ovoid LV in diastole. The septal thickness in diastole is 10.5mms, and bulges toward the RV while the free wall dimension is 6.6 mms. The LV cavity measures 5.3cms which is upper limits normal.
Ashley Davidoff MD
Nulling the Myocardium
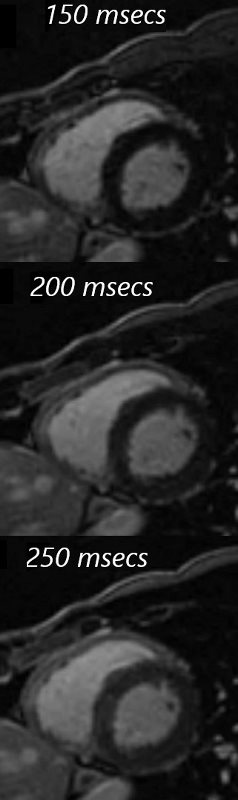
Nulling evaluation using short axis IR sequences shows an example of optimal numbing at a TR of 150 msecs. The myocardium is diffusely black or nulled at this TR . At 200 msecs there is intermediate nulling and at 250 msecs nulling is poor with a gray rather than a black myocardium.
Ashley Davidoff MD
Short Axis View Post Nulling
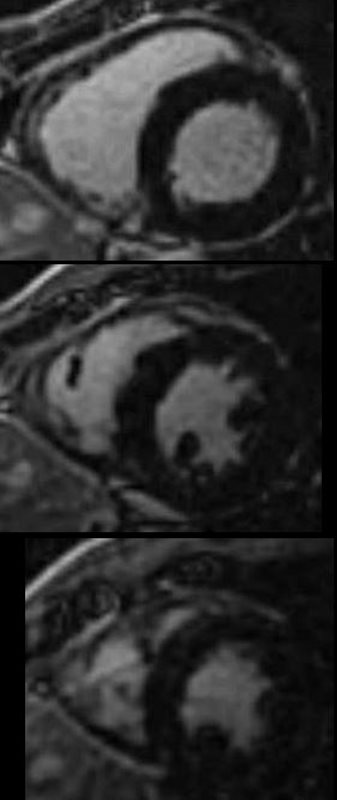
The delayed gadolinium (LGE) sequences using short axis at a TR of 150msecs shows no evidence of LGE from the base of the heart (upper image) mid body (middle image) and apex (lower image).
There are some vague nodular changes in the mid myocardium on the inferior wall (middle image) and in the septum (lower image) but these are not verified in the long axis views and are thought to represent artifact
Ashley Davidoff MD
Parasagittal View of the RV
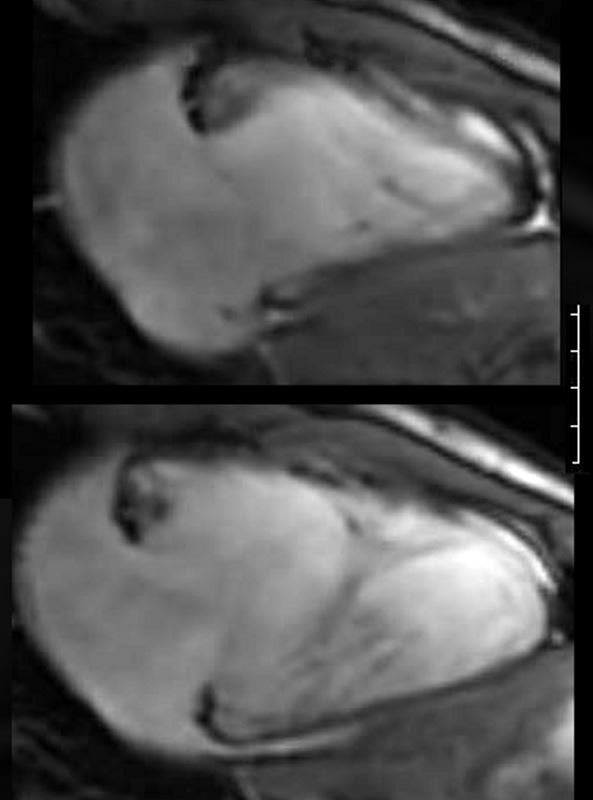
White blood imaging of the RV shows a normal sized triangular RV in systole (above) and diastole (below). The walls appear normal thickness in the diastolic image, and the approximate volume of the RV in systole is just about 1/3 that of the volume in diastole suggesting a normal EF. There is no dyskinesis
Ashley Davidoff MD
Sagittal View of the RV and RVOT
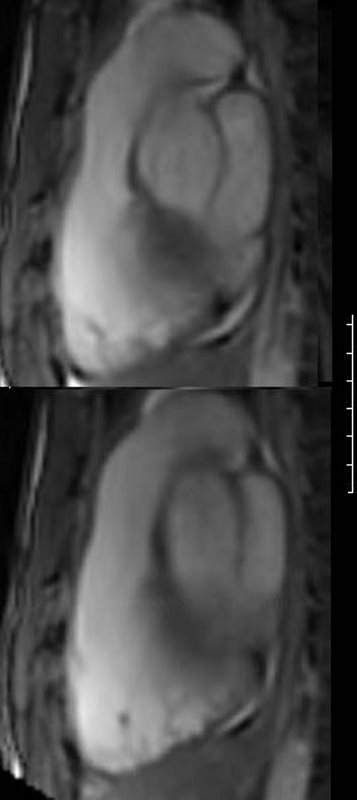
White blood imaging of the RV in the sagittal view shows a normal sized triangular RV in systole (above) and diastole (below). The walls appear normal thickness in the diastolic and systolic images. The RVOT and infundibulum also contract during systole (upper image). The MPA is normal. There is no dyskinesis
Ashley Davidoff MD
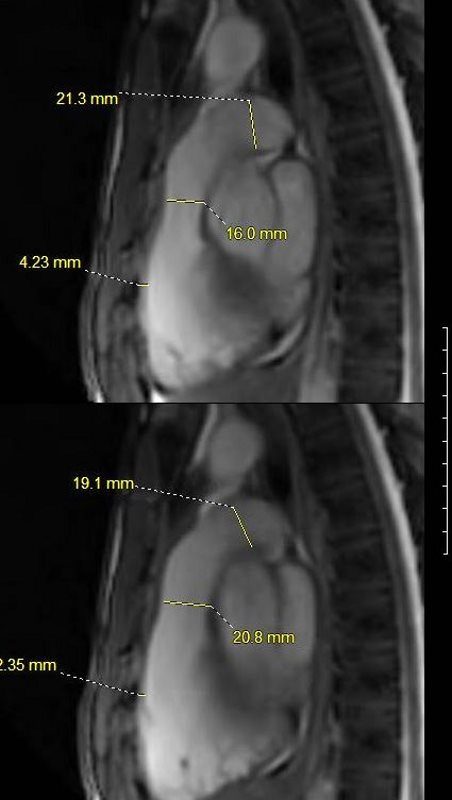
White blood imaging of the RV in the sagittal view shows a normal sized triangular RV in systole (above) and diastole (below). The walls appear normal thickness in the diastolic image, 2.4mm (anterior wall). Note the systolic contraction of the RVOT changing from 1.6cms in systole (above) to 2.1cms in diastole below. The MPA measures 19mm. There is no dyskinesis
Ashley Davidoff MD
Axial View of the MPA and Ascending Aorta
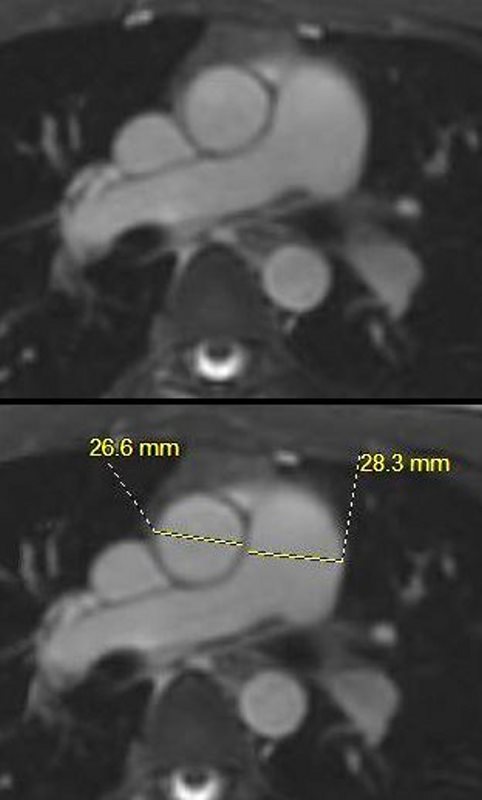
White blood imaging of the MPA and tubular portion of the ascending aorta at the level of the MPA bifurcation in the axial projection shows a normal sized MPA measuring 2.8cms (normal up to 3cms). The tubular portion of the ascending aorta measures 2.7cms (normal up to 3.5cms
Ashley Davidoff MD
Axial View of the LA

White blood imaging of the LA in the axial projection shows a normal sized LA measuring 1.7cms (normal up to 4cms). In this plane the LA is relatively small, but normal. It is usually slightly larger than the proximal ascending aorta at this level. The aorta measures 2.3cms. Note the rectangular shape of the LA.
Ashley Davidoff MD
Axial View of the of the RA, RV, and LV
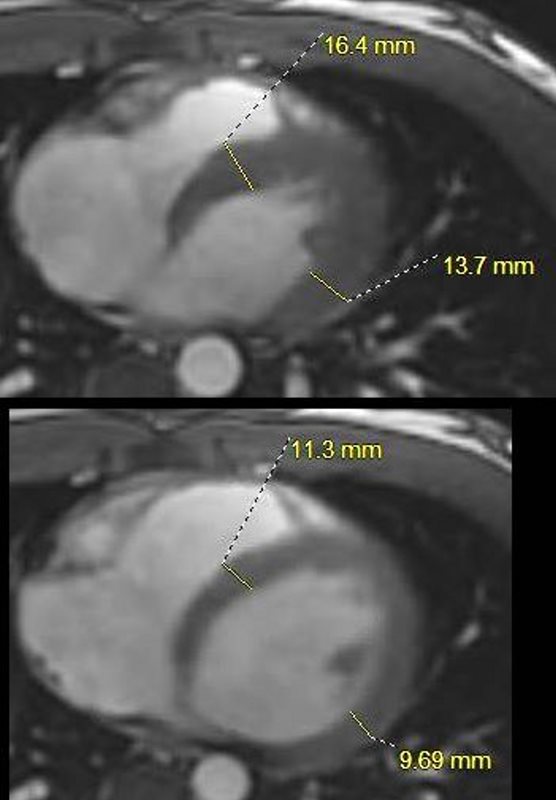
White blood imaging of the LV in the axial projection in systole above and diastole below. In diastole the septum measures 1.1cms and the free wall measures 9.7mms (normal +/- 1.2- 1.4 cms).
Ashley Davidoff MD
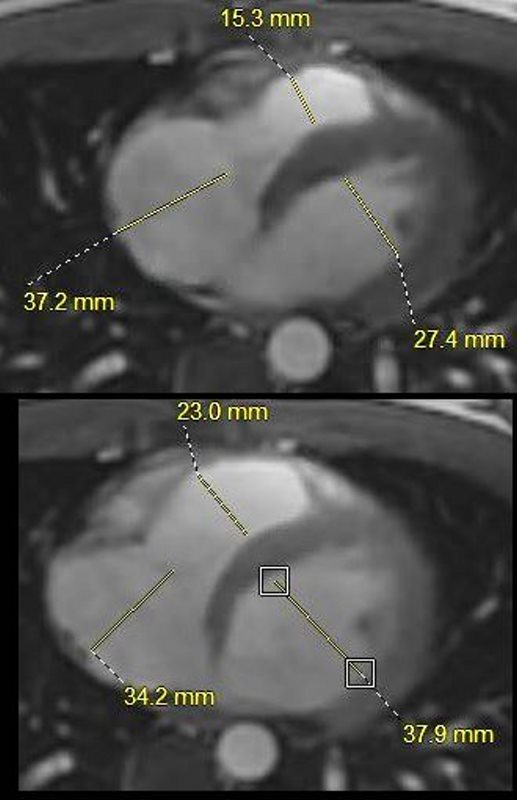
This is the MRI of a 19-year-old male who presented with syncope and the study was performed to identify a possible arrhythmogenic focus
White blood imaging of the RA, LV and RV in the axial projection in systole above and diastole below. In diastole the RA measures 3.4cms (n= up to about 5cms) the RV measures 2.3cms (n= up to about 4 or 4.5cms) and the LV wall measures 3.8cms (normal up to 5 or 5.5cms). The volume of the RV is about 2/3 the size of the LV and the RA volume appears about 1/3 the size of the RV.
Ashley Davidoff MD
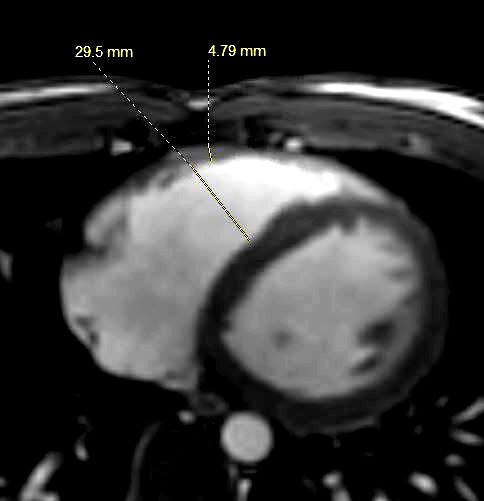
This is the MRI of a 19-year-old male who presented with syncope and the study was performed to identify a possible arrhythmogenic focus
White blood imaging of the RV in the axial projection in diastole shows a transverse diameter of the RV of 2.95cms., (up to 4-5cms) which is normal and an RV wall thickness 4.8mm (normal up to about 5mms. ) The volume of the RV is about 2/3 the size of the LV.
Ashley Davidoff MD