-
Indications
-

Current Guidelines for Calcium Score 2018 - https://heart.thecommonvein.net/95h-normal-calcium-score-normal-coronaries/
-
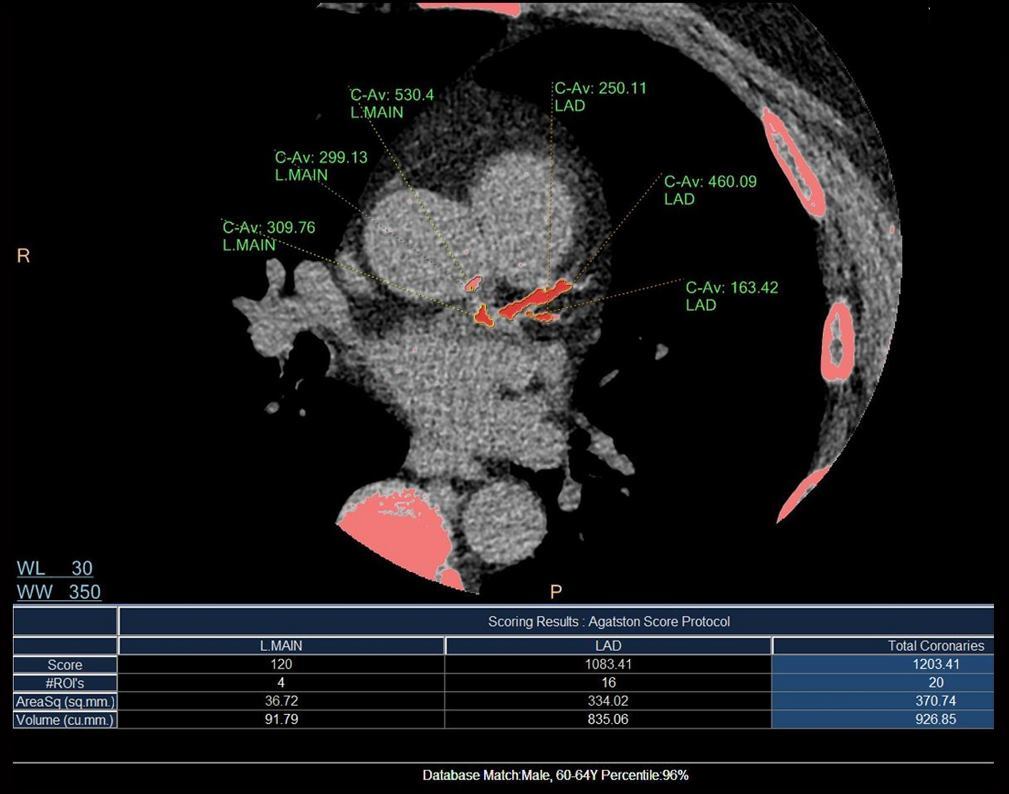
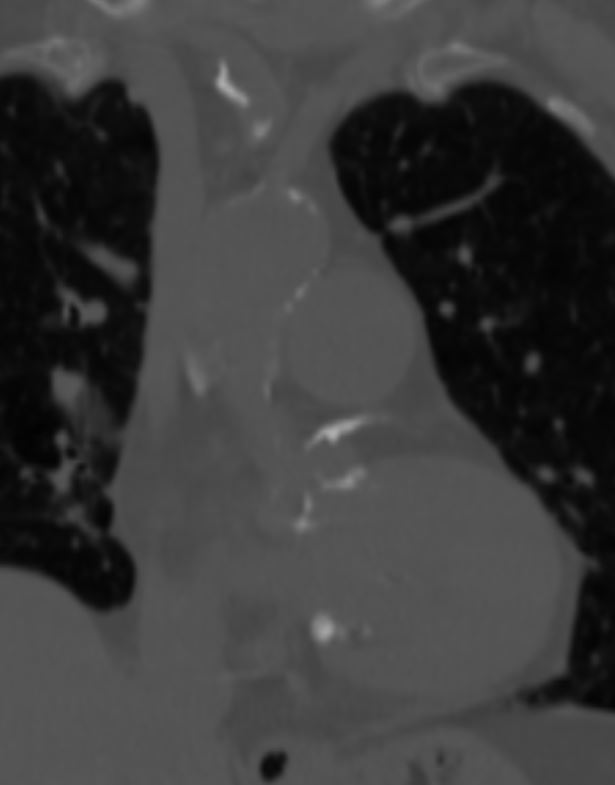
62 year old male with atypical chest pain
CT calcium score shows heavy calcification in the LAD but also involving the left main with a total score 1203 which is the 96th percentile for his age and sex
Ashley Davidoff MD
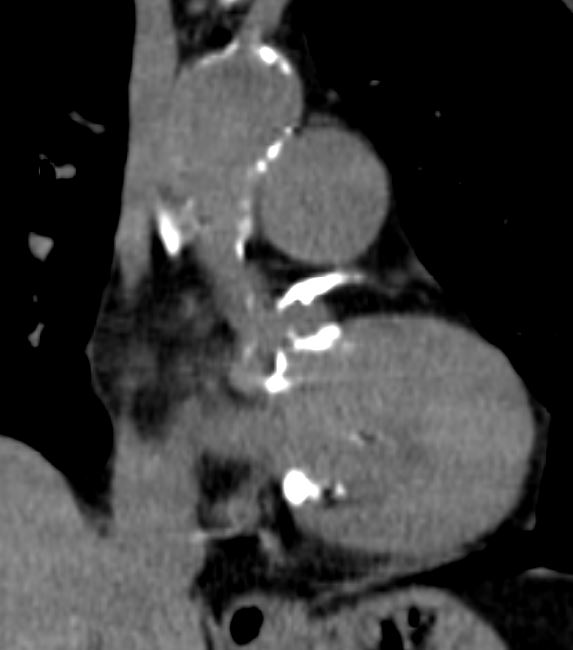
thecommonvein.net - 41 year old male with significant family history
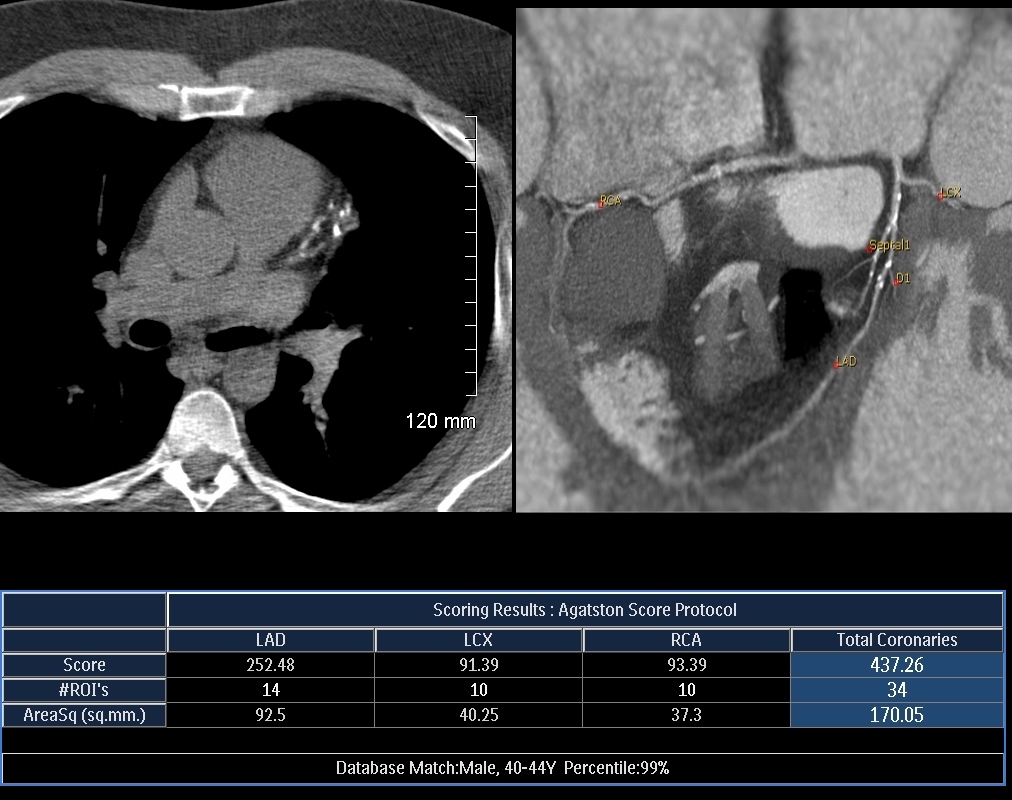
41 year old male with significant family history
CT calcium score shows spotty foci of calcification with a total score of 437 which is the 99th percentile for his age and sex
Ashley Davidoff MD
thecommonvein.net -
Definition
- preventive tool
- used to identify calcific atheroscleosis
-
BAckground
- Approximately 50% of all cardiovascular disease (CVD)–related deaths
- no prior cardiac symptoms or diagnoses,
- Approximately 50% of all cardiovascular disease (CVD)–related deaths
-
Aim
- Identify the presence of atherosclerosis in
- patients in whom management may change
- ie those wh would benefit for conservative preventive management
- positive family history
- ACC Risk Calculator
- categorised
- low-risk,
- intermediate-risk, and h
- igh-risk for future heart attacks.
- ie those wh would benefit for conservative preventive management
-
Indications
-
- Smoking,
- Obesity,
- hypercholesterolemia
- hypertension,
- diabetes
- sedentary lifestyl
- positive family history of myocardial infarction,
- inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes.
-
Calcium score should be considered in people between 45-70 years of age.
-
Under 40, the zero score’s negative predictive value is not high since there has not been enough time for the lipid-rich-plaques to calcify.
- Above 70,
- nearly everyone has calcification of the coronary arteries.
- positive unless significantly elevated,
- not necessarily signify high risk.
- calcium score of 0
- very high negative predictive value.
- positive unless significantly elevated,
- nearly everyone has calcification of the coronary arteries.
-
-
Contraindications
- Relative
- very low pretest probability
- very high CV risk
- since they prevention Rx anyway
- Relative
-
Advantages
- High sensitivity for atherosclerosis
- low radiation 1mSV
- the more burden the more benefit with conservative therapy
- statins
-
Disadvantages
- Radiation
-
Method
-
Patient Prep
-
Technique
- Gated
- Multi
-
-
Results
-
- Report should include
- the absolute Agatston score and the
- age, sex, and race-specific CAC percentile;
- the number of vessels with CAC;
- the presence of CAC in the left main coronary artery;
- specific highlighting of individuals with very high CAC scores of greater than 1000
- Test of plaque burden
- A calcium score of 20 in a
- 70-year-old person is low but in a
- 35-40-year-old is significantly ele
- should be considered considerably elevated.
- Report should include
-
Conclusions
- Discussion
- In a patient with negative calcium score – we do not know if there is fibrofatty plaque
- A high coronary calcium score can change someone’s risk from low to high but not the other way. A low or even zero calcium score does not change the status of a high-risk patient to a low-risk. A “high risk” individual will remain “high risk” regardless of their calcium score.
- calcium score should always be interpreted in the
- context of other risk factors
- never solely.
- 0 in a low-risk patient is highly reassuring.
- 0 in high risk patient
- smokes
- high cholesterol or
- high blood pressure
- is less predictive.
- Associated diseases with high calcium score
- cancer
- Incidental Finding
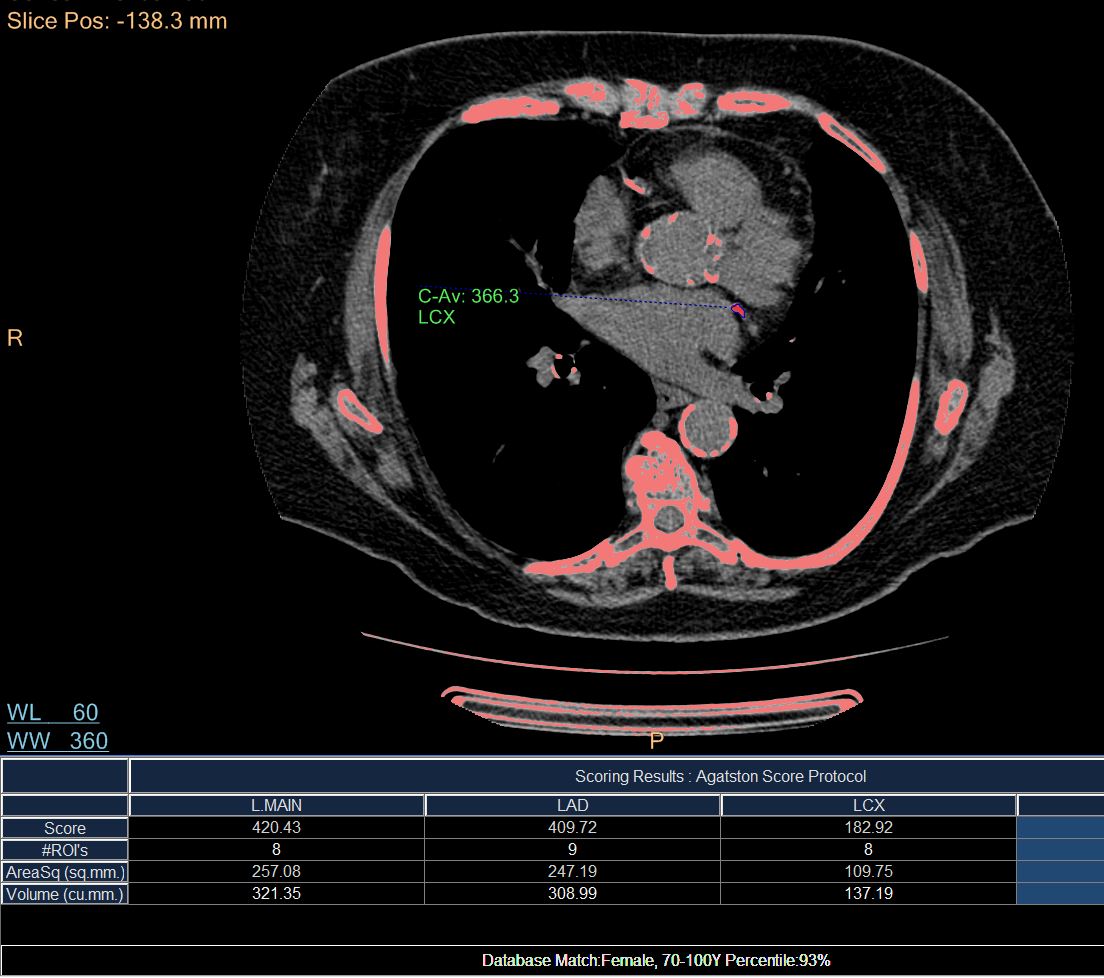


-
Links and References
- Journal Articles
- Patel, J et al Assessment of Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring to Guide Statin Therapy Allocation According to Risk-Enhancing FactorsThe Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
- Videos
- Blaha Michael Yale Grand Rounds 2022
- Medcape MedPage Peer to Peer Philip Green
- Guidelines
- 2022
- Journal Articles