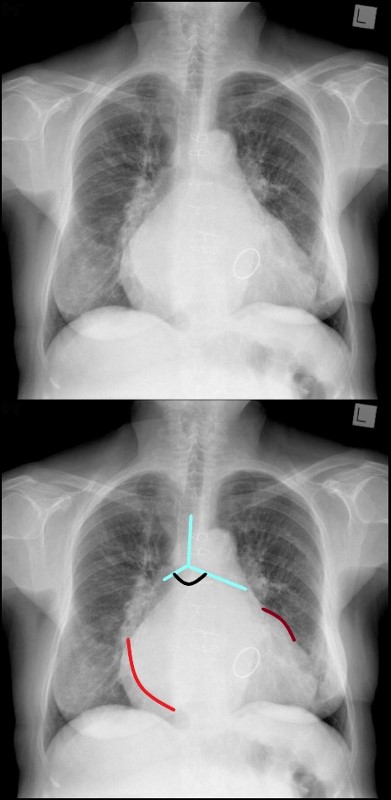
The frontal CXR demonstrates findings consistent with mitral stenosis including a widened carinal angle (teal blue and black arc), a double density (red arc) and an enlarged left atrial appendage (maroon arc).
The overall shape of the heart is triangular suggesting right ventricular enlargement. A mitral valve prosthesis is in position
Courtesy of Radiopaedia
Ashley Davidoff MD
Reference values for quantitative left
ventricular and left atrial measurements
in cardiac computed tomography
Eur Radiol (2008) 18: 1625–1634
Left Atrial Diameter
- normal left atrial AP diameter
- women: <4.0 cm
- men: <4.1 cm
An accurate AP measurement is made on the three-chamber view on a gated cardiac CT. The AP left atrial diameter on a non-gated contrast-enhanced CT can only be an estimate since foreshortening of the chamber and the cardiac cycle cannot be accounted for.
Atrial volume measurements are considered more accurate than either AP or area measurements.
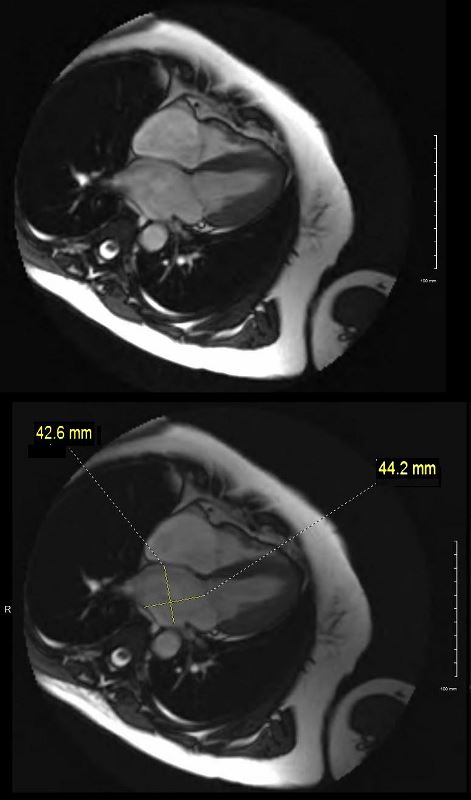
Ashley Davidoff MD
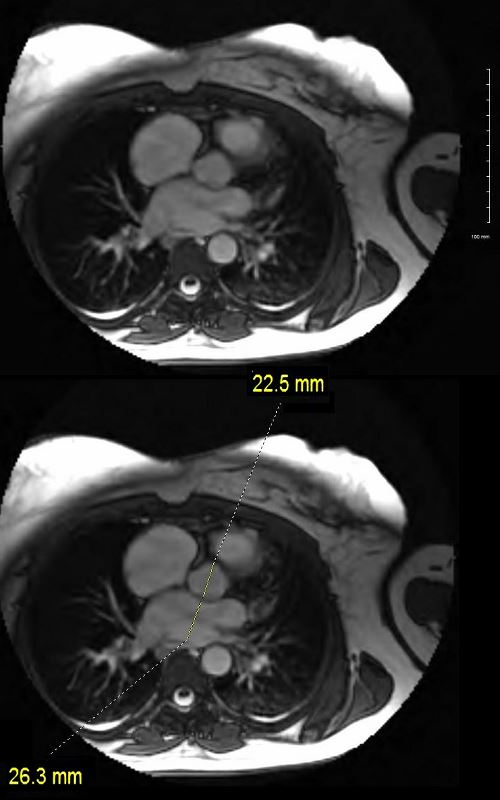
Ashley Davidoff MD
Left Atrial Volume
The atrial volume can be calculated with: 8/3π[(area of the four chamber view)*(area of the two chamber view)/(shortest inferior-superior length from the annular plane to the back wall of the atrium)]
- normal atrial volume
- women: <53 mL
- men: <59 mL
Enlarged Left Atrium
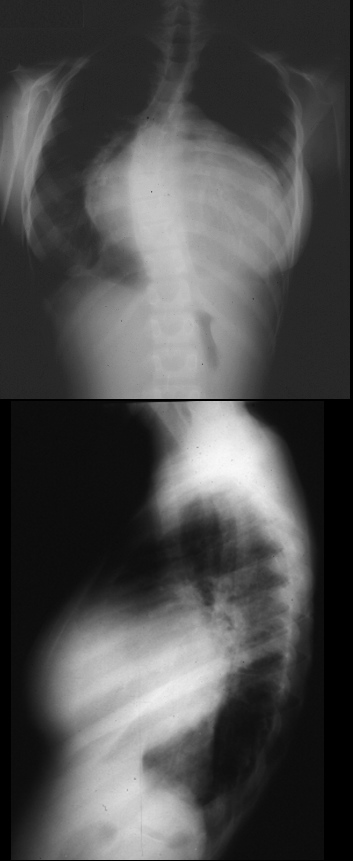
35 year old patient with severe mitral stenosis . with left atrial enlargement (LAE) characterized by elevation of the left mainstem bronchus, straightening of the left heart border, and prominence of the upper 1/3 of the posterior border of the heart. The right atrium is also enlarged characterized by a rotund right heart border. There is right ventricular enlargement characterized by filling in of the retrosternal airspace.
Ashley Davidoff MD

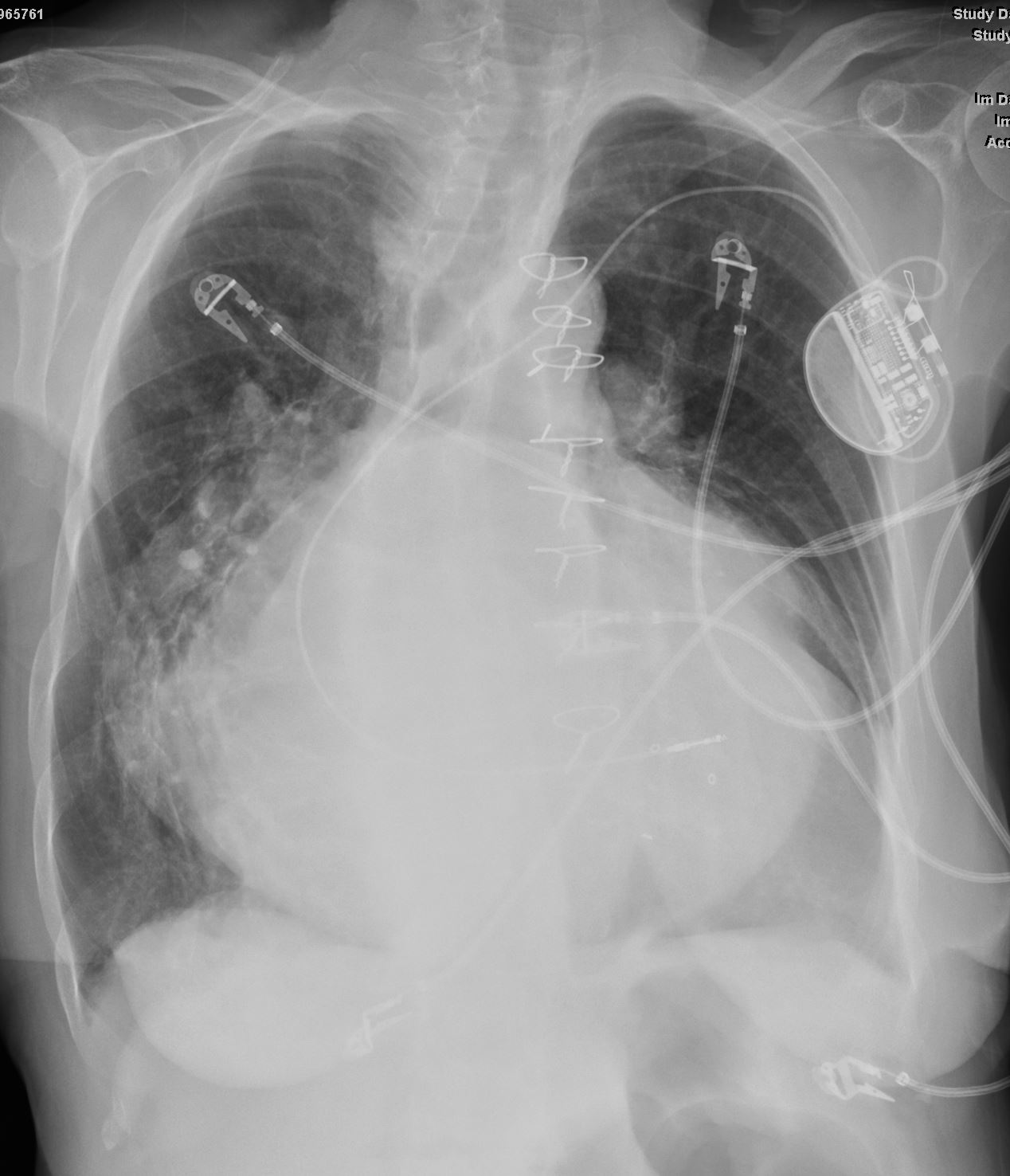
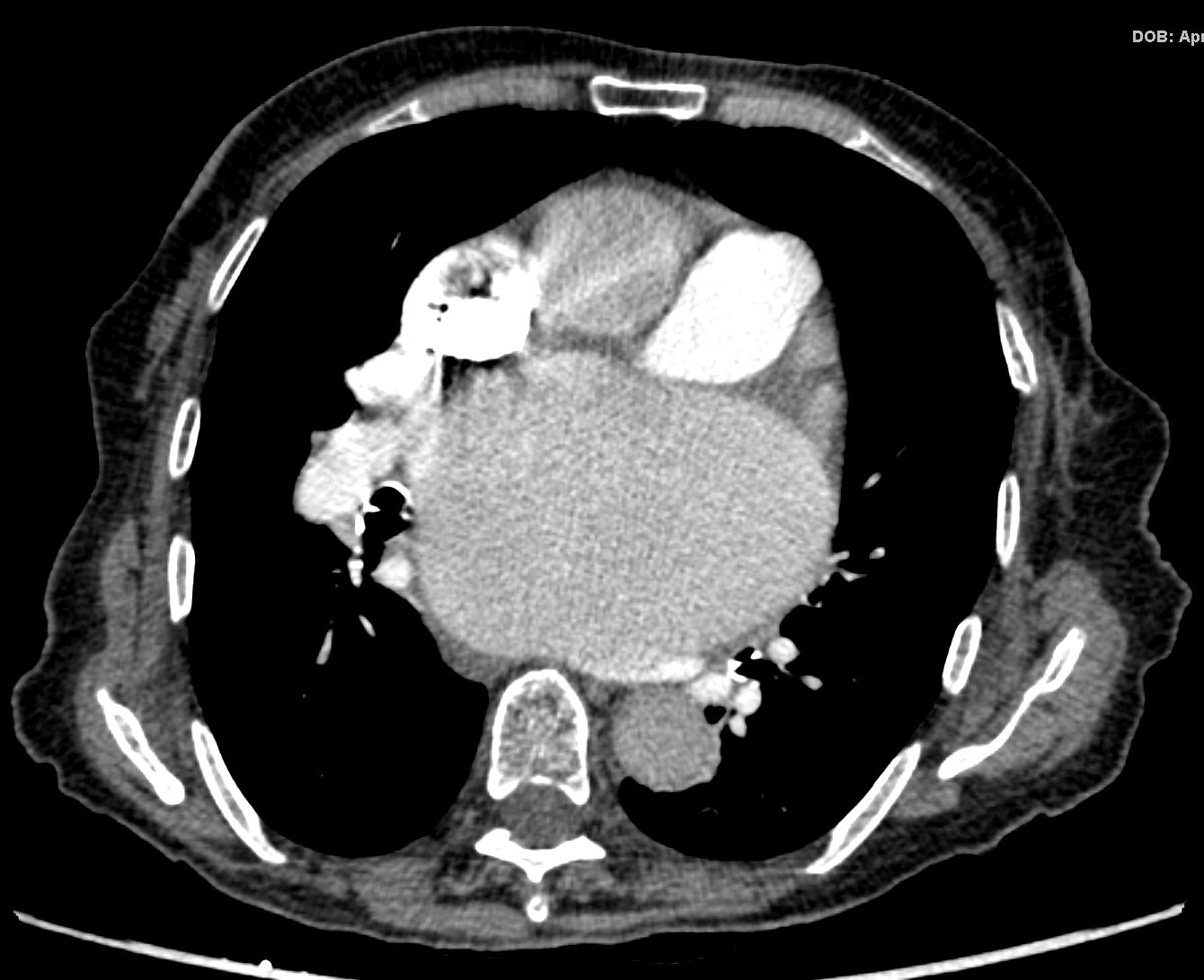
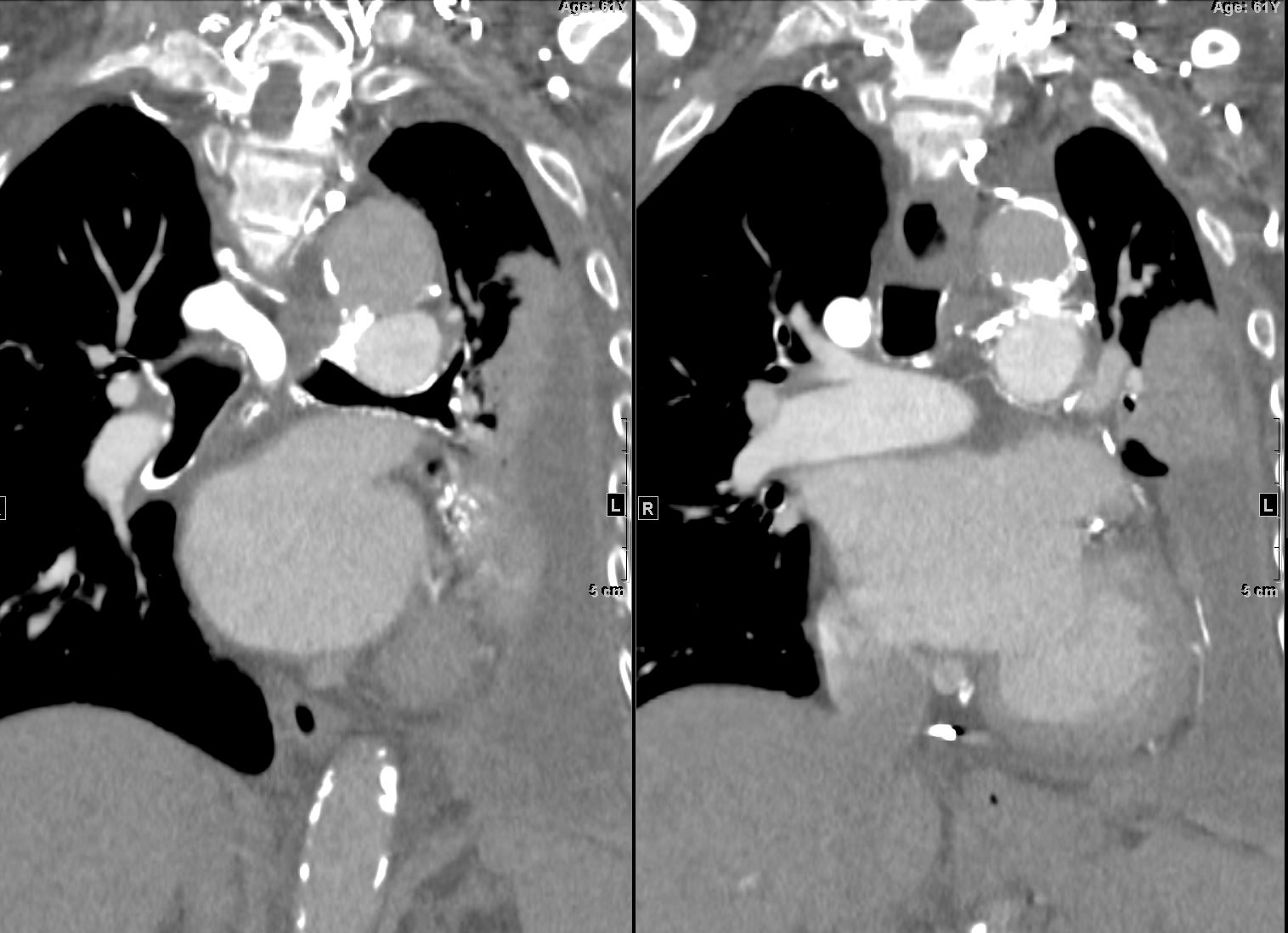
87 year old male with findings consistent with mitral stenosis , characterised by calcified mitral valve, enlarged left atrium, normal sized left ventricle,with enlarged right atrium, right ventricle and main pulmonary artery.
Pure mitral stenosis is most commonly caused by rheumatic heart disease
Ashley Davidoff MD

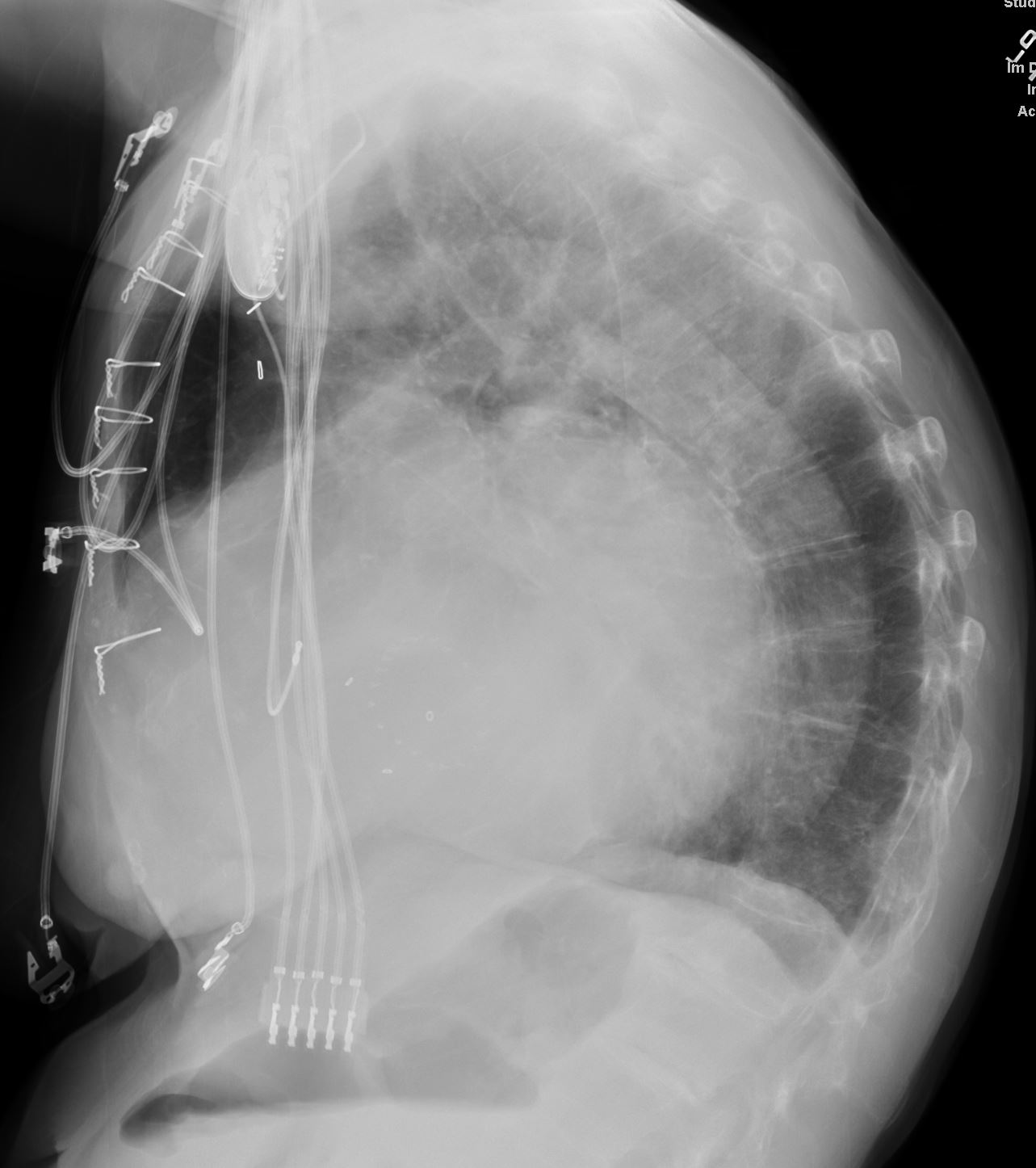
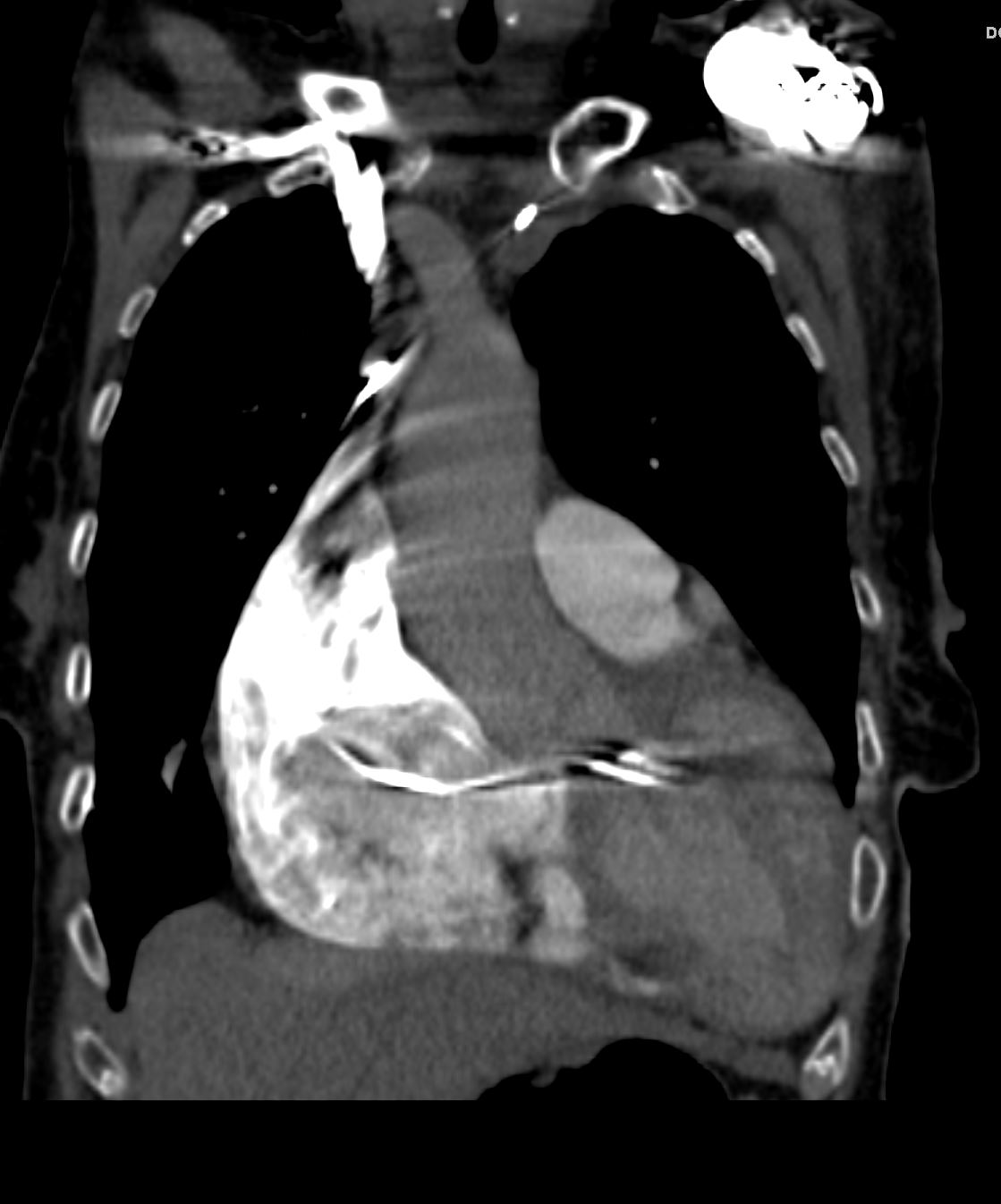
87 year old male with findings consistent with mitral stenosis , characterised by calcified mitral valve, enlarged left atrium, normal sized left ventricle,with enlarged right atrium, right ventricle and main pulmonary artery.
Pure mitral stenosis is most commonly caused by rheumatic heart disease
Ashley Davidoff MD
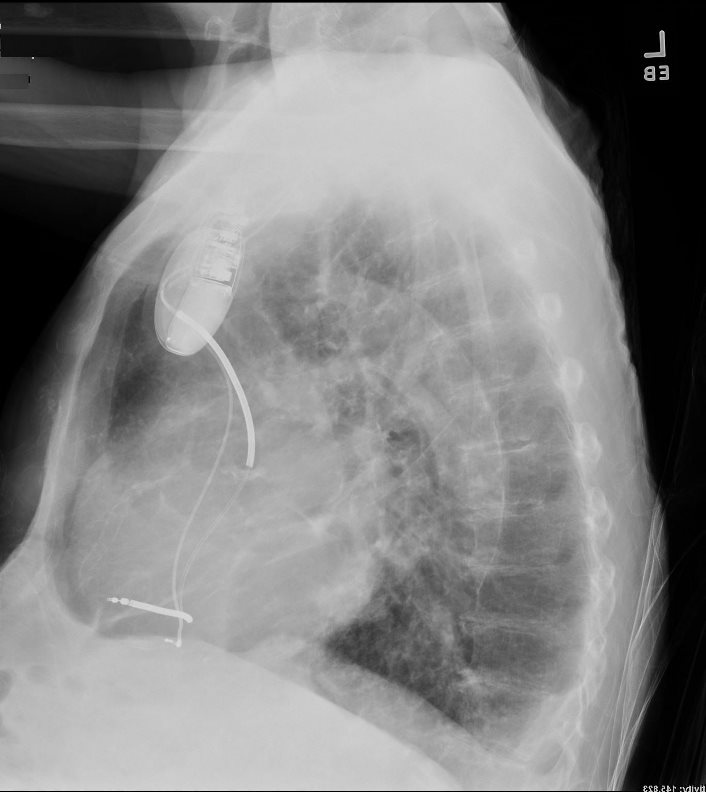
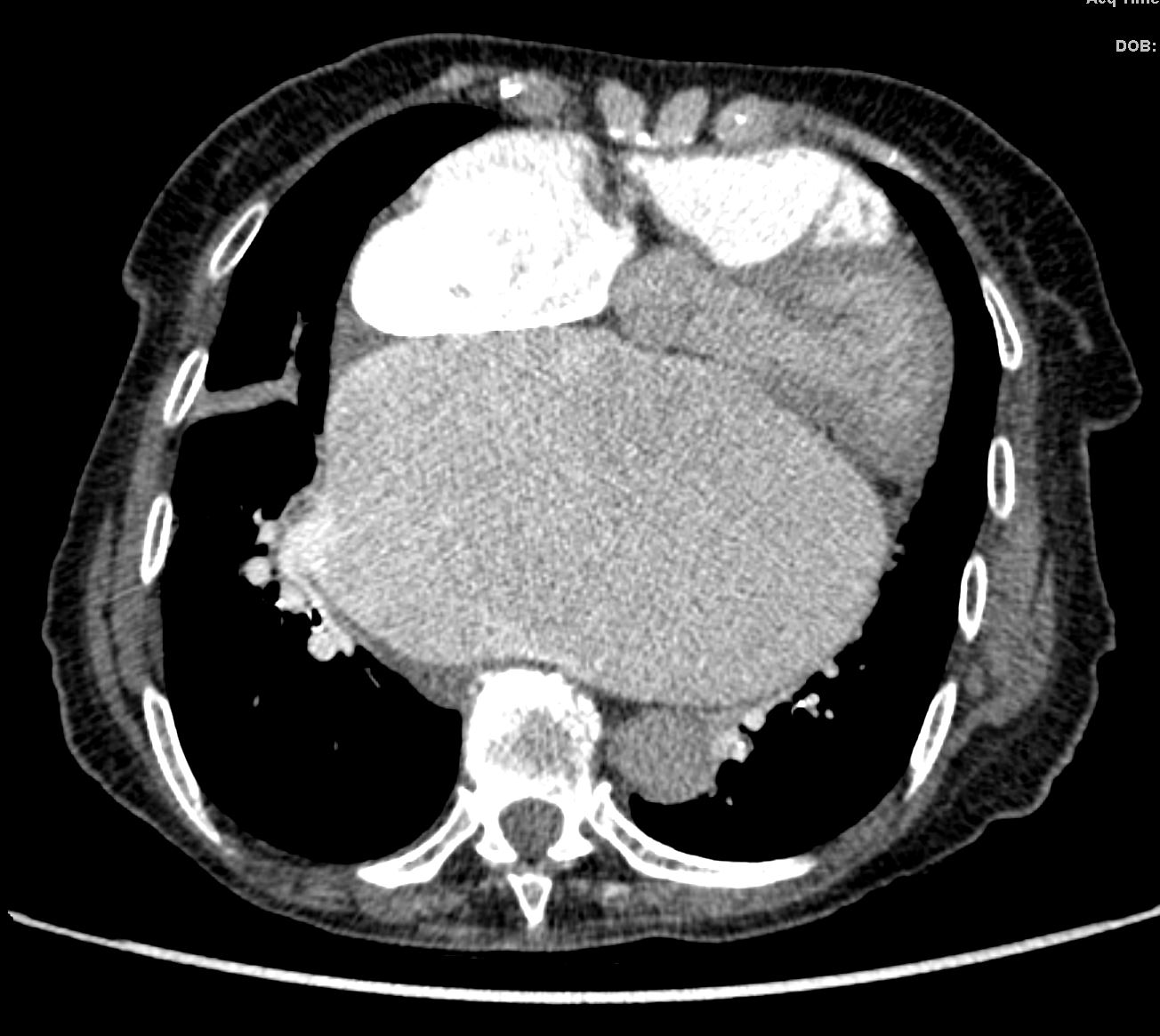
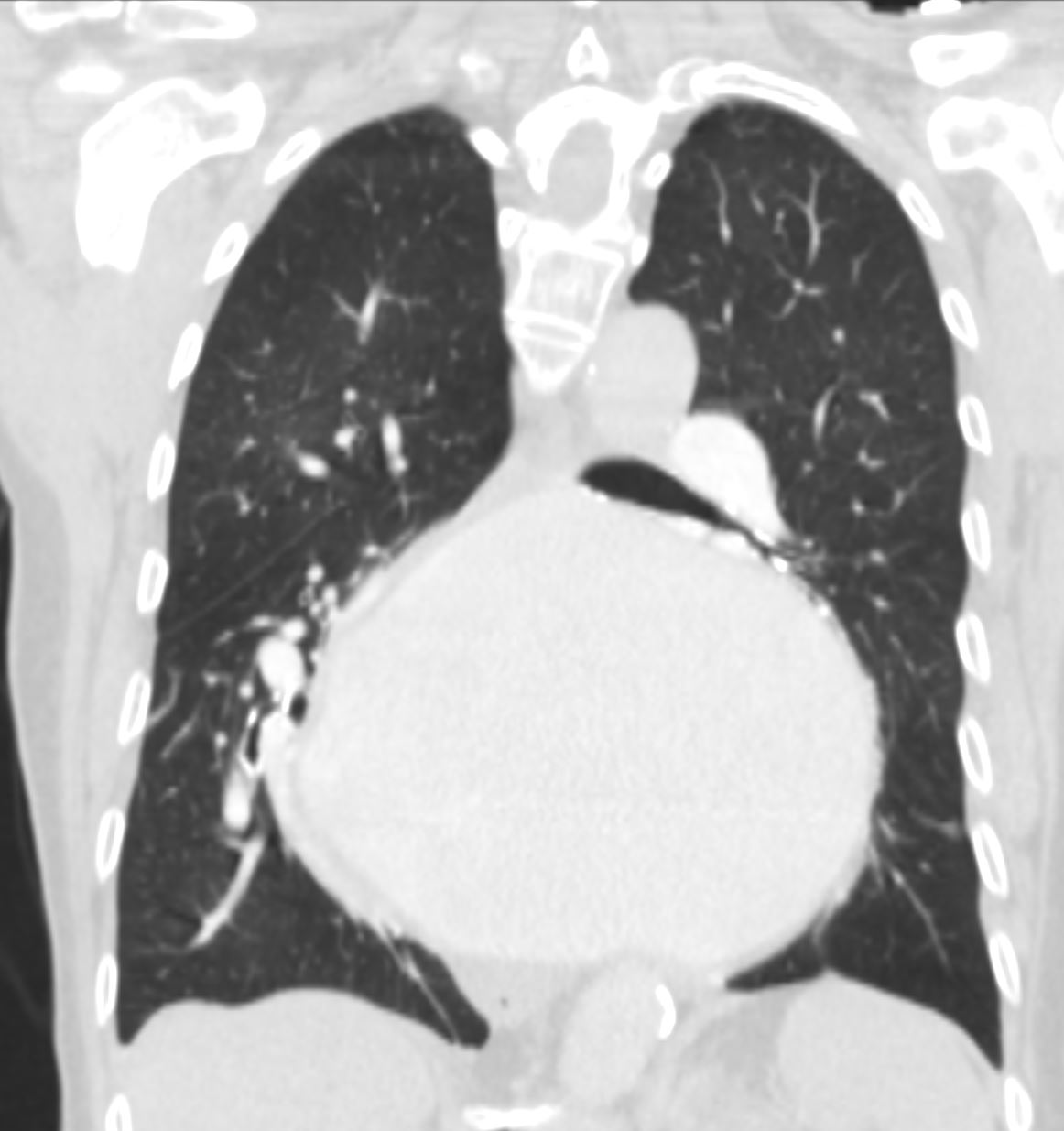
87 year old male with findings consistent with mitral stenosis , characterised by calcified mitral valve, enlarged left atrium, normal sized left ventricle,with enlarged right atrium, right ventricle and main pulmonary artery.
Pure mitral stenosis is most commonly caused by rheumatic heart disease
Ashley Davidoff MD
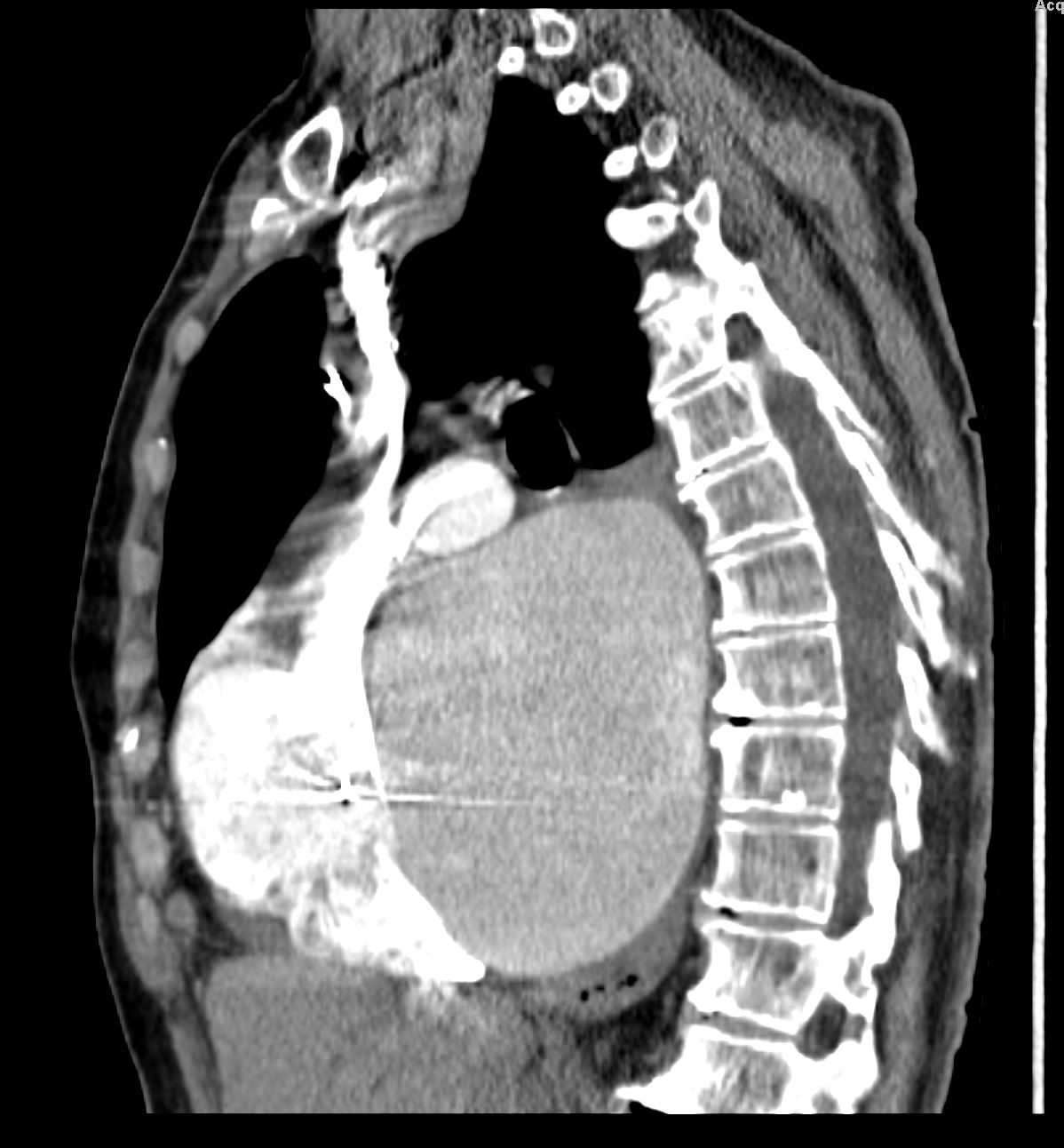
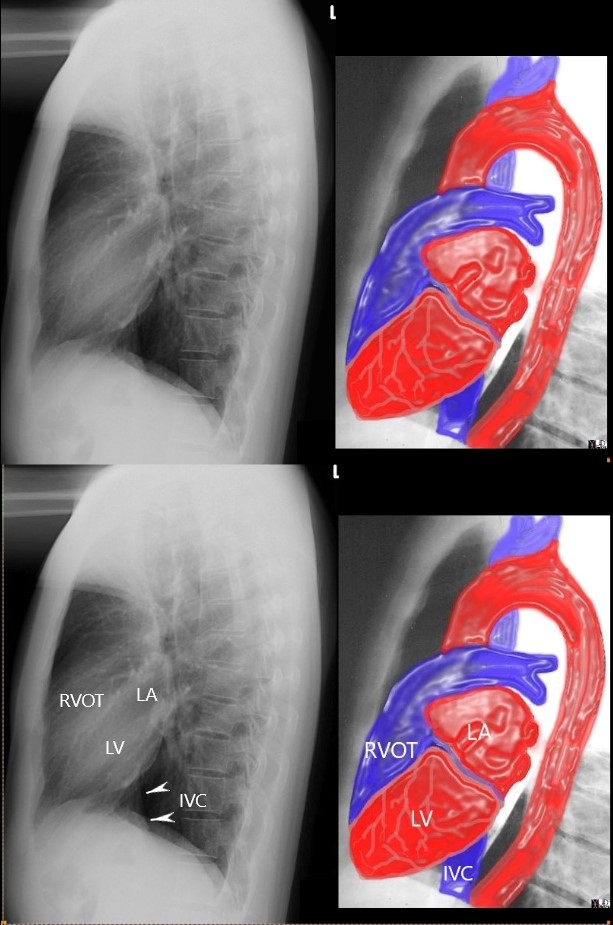
LAA pushing on Left MAin Bronchus
References and Links
- TCV
- 001H Probable Sarcoidosis LAE MR
- 003 Non Compaction Heart Failure and Pacemaker
014 87M with Rheumatic Mitral Stenosis
044H Atrial Myxoma LAE and PAH masquerading as MS - 045H Calcified Atrial Myxoma LAE