LV Mass and LV Mass Index
Left ventricular mass and left ventricular mass indexed to body surface area estimated by LV cavity dimension and wall thickness at end-diastole.
In a Nutshell
Mass: Normal 90 -100 gm/m2
Method
- Evaluation on short axis parallel to the true LV short axis
- LV mass is measured at a single time point within the cardiac cycle (the standard is end-diastole)
- single breath-hold removes respiratory artifact.
- About 10 slices will cover the ventricle,
- Simpson’s method (“stack of disks”)
- calculated from the
- product of the myocardial volume
- difference between the epicardial and endocardial LV volumes by a semi-three dimensional data set
- specific gravity of heart muscle (1.05 g/ml).
- product of the myocardial volume
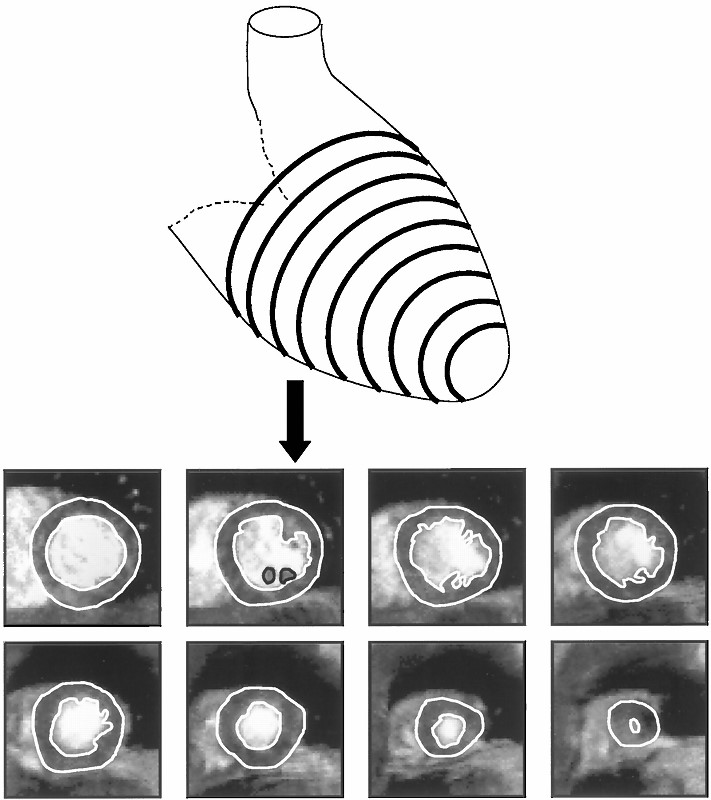
Diagrammatic representation of the LV with typical CMR short axis images obtained.
Myerson,S et al Assessment of Left Ventricular Mass by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
Hypertension Vol. 39, No. 3 2002
Normal Values have such a wide range depending on sex age and race – Echo and MR measurement are fairly consistent
Females about 60 g/m2
Males about 70 g/m2
LV mass was significantly higher in males compared to females (mean ± SD of 53 ± 9 g/m2 vs 42 ± 7 g/m2). Petersen et al JCMR
Normal values of LV mass indexed to body surface area were found to be 70 (+/- 6-9 g/m2 in men and 61 (+/- 6 -8 g/m2 in women. Mizukoshi, showed echo and MR good correlation
Normal values of LV mass indexed to body surface area were found to be 60 (+/- 9 g/m2 in men and 49 (+/- 7 g/m2 in women). Fuchs EHJ CV Imaging
Reference Ranges & Partition Values for LV Mass Indexed To BSA (g/m2)
| Female | Male | |
| Reference Range | 43-95 | 49-115 |
| Mildly Abnormal | 96-108 | 116-131 |
| Moderately Abnormal | 109-121 | 132-148 |
| Severely Abnormal | ≥122 | ≥149 |
Mizukoshi, Left ventricular mass quantitation using single-phase cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Cardiol. 1992 Jul 15;70(2):259-62.
Mizukoshi, MD, et al CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS
LEFT VENTRICULAR MASS AND FUNCTION
Normal Values of Left Ventricular Mass Index Assessed
by Transthoracic Three-Dimensional
Echocardiography