Reprinted from [46] with permission from BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
ikeda et al Isolated left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy in adults Journal of Cardiology
Volume 65, Issue 2, February 2015
- Non-compaction of the left ventricle,
aka- spongiform cardiomyopathy or
left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC)
- spongiform cardiomyopathy or
- is a congenital abnormality
- caused by
- embryological arrest of normal myocardial compaction of
- hypertrophic ventricular trabeculations and
- deep interventricular recesses.
- acquired cases have also been reported.
Radiographic features
Echocardiography
- Cardiac MRI
- modality of choice
- Size
-
- ratio of non-compacted telediastolic myocardium to compacted myocardium of
- more than 2.3:1 (sensitivity: 86%, specificity: 99%).
- ratio of non-compacted telediastolic myocardium to compacted myocardium of
-
- Position
- predominantly affects the
- inferolateral walls and the
- apex
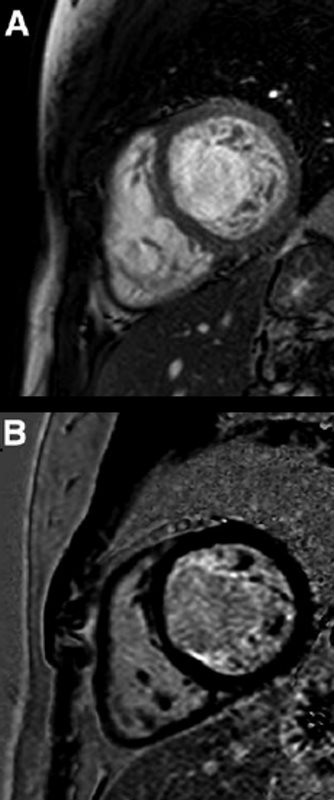
LGE in NON COMPACTION
Short-axis precontrast (A) and delayed enhancement (B) views of a patient with noncompaction cardiomyopathy. On precontrast view, non-compacted layer of LV myocardium is visible. Late gadolinium enhancement sequence demonstrated fibrosis of trabecules of non-compacted layer.
Panovsky et al The prognostic impact of myocardial late gadolinium enhancement.
Cardiology in Review · May 2014
- predominantly affects the
Other commonly associated features include:
- left ventricular dysfunction
- both systolic and diastolic
- intraventricular thrombus
- left atrial enlargement
- associated with atrial fibrillation
Treatment and prognosis
The only definitive treatment of left ventricular non-compaction is cardiac transplantation. Otherwise, prevention of both heart failure and thromboembolic events are the main target of treatments.
Differential diagnosis
Possible differential considerations in certain situations include: