Copyright 2008
Principles
Structure
Single common vein during embryology (4th week gestation) incorporated into the left dorsal atrium with 70% of patients having 4 pulmonary veins left superior (LS) left inferior (LI) right superior (RS) and right inferior (RI) which usually accommodates the middle lobe vein). The myocardium of the left atrium extends over the pulmonary vein for 1-2cms.
Congenital anomalies occur when there is over incorporation or under incorporation

Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
77612b.3kb07.8s
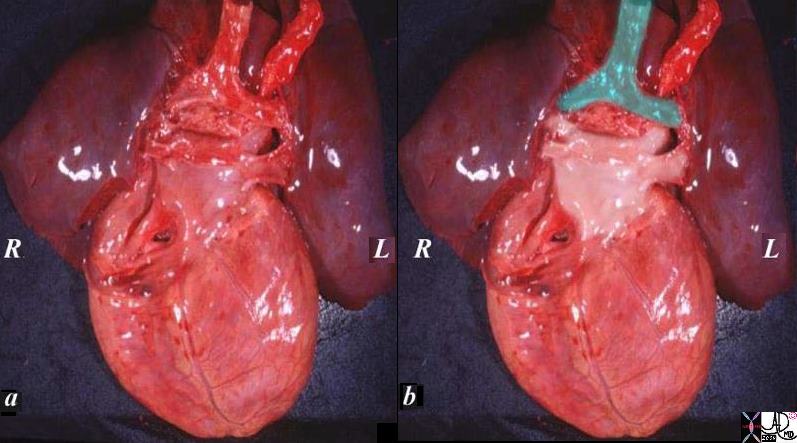
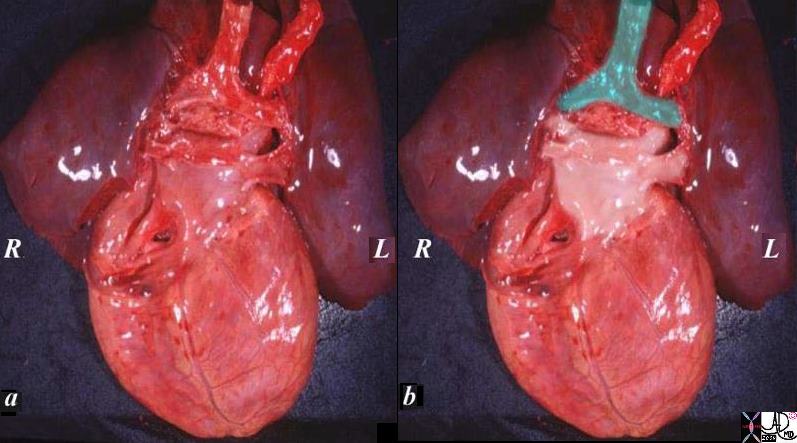
The specimen of heart and lungs is examined from posteriorly with the left atrium and 4 pulmonary veins. (overlaid in pearl white) The trachea and bronchi are intact (green). The left atrium lies just below in the angle of the carina.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
08376c02.82s
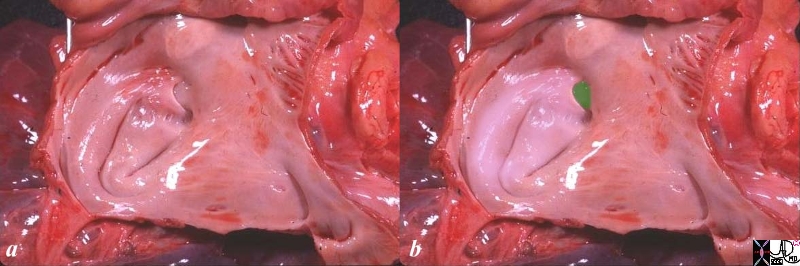
The anatomic specimen has been opened from its posterior aspect revealing a relatively smooth walled inner lining. The left atrial appendage(laa) has been opened revealing fine pectinate muscles. 5 pulmonary veins are seen entering the left atrium, with 2 entering from the left lower vein. The atrial septum with fossa ovalis and foramen ovale are smooth except for the “u” shaped upper border of the septum primum that allows identification of the left atrium. the glistening surface of the endothelium is exemplified in this image.
Ashley Davidoff
TheCommonVein.net
06426c01.81s
Size
SPV ostia larger
|
ostia (cms) |
1cms from ostia (cms) |
|
|
RSPV |
1.7 +/-.24 cms |
1.4 +/-.21 cms |
|
RIPV |
1.59+/- .25 cms |
1.16 +/-.25 cms |
|
LSPV |
1.76 +/-.41 cms |
1.45 +/-.32 cms |
|
LIPV |
1.39 +/- .29 cms |
1.23 +/-.24 cms |
More commonly on left over incorporation
supernumerary R>L
Shape
Left pulmonary veins are oval ostia oval
Right pulmonary vein ostia are circular
Position
Usually right middle lobe vein drains into right superior vein in 70% directly into LA 20% and 5% intp RIPV
Lingula vein usually arises from the left superior pulmonary vein.
In 10-25% patients there is a single vein on one side. This is more common on the left
|
LA and Pulmonary Veins from Posterior |
| The specimen of heart and lungs is examined from posteriorly with the left atrium and 4 pulmonary veins. (overlaid in pearl white) The trachea and bronchi are intact (green). The left atrium lies just below in the angle of the carina.
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff copyright 2009 all rights reserved 08376c02.82s |
|
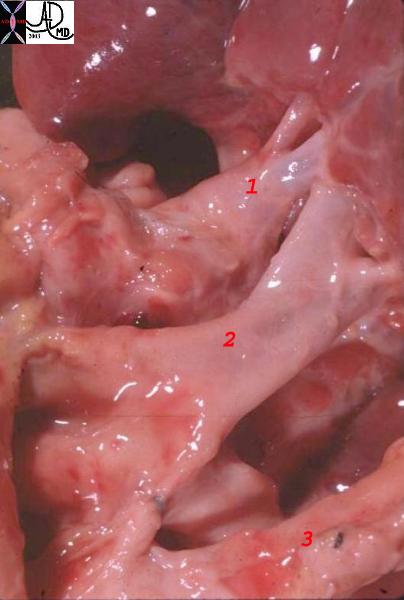
Posterior View Veins and Arteries |
| This normal anatomic specimen from a posterior aspect showing the LPA (1) and upper lobe pulmonary veins (2) and lower lobe pulmonary veins (3) shows the left pulmonary veins (1) and left pulmonary artery. The two veins to one artery is the usual. Venous inflow must of course equal arterial outflow and so each vein carries about half the load and are about half the size of the main branch pulmonary artery
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. 06881labelled |
|
Anatomy of the Left Atrium |
|
The anatomic specimen has been opened from its posterior aspect revealing a relatively smooth walled inner lining. The left atrial appendage(laa) has been opened revealing fine pectinate muscles. 5 pulmonary veins are seen entering the left atrium, with 2 entering from the left lower vein. The atrial septum with fossa ovalis and foramen ovale are smooth except for the “u” shaped upper border of the septum primum tha allows identification of the left atrium. the glistening surface of the endothelium is exemplified in this image. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff copyright 2009 all rights reserved 06426c01.81s |
|
Diagram of the Secondary Lobule Veins and Lymphatics Travel Together |
| The arteries and airways pair up and travel together down the respiratory tree branching in exactly the same way until they reach the pulmonary lobule. The pulmonary lobule, also called the secondary lobule is a structural unit surrounded by a membrane of connective tissue, and it is smaller than a subsegment of lung but larger than an acinus. This diagram shows two secondary lobules lying side by side. The pulmonary arteriole (royal blue) and bronchiole (teal) are shown together in the centre of the lobule (“centrilobular”), with two other pairs of bronchovascular bundles, while the oxygenated pulmonary venules (red) and lymphatics (yellow) are peripheral and also form formidable and almost inseparable pairs. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD art code lung secondary lobule bronchovascular bundle centrilobular polyhedral drawing normal anatomy histology 42440b08 |
|
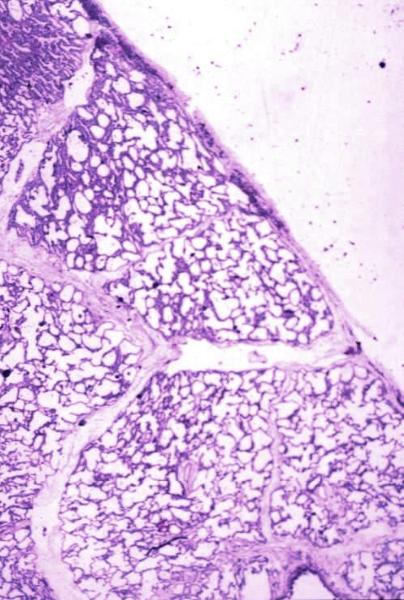
Secondary Lobule and Interlobular Septa |
| Normal lung histology This image is a panoramic view of the lung showing secondary lobules and interlobular septa. Within the interalveolar septae, one sees small venules and lymphatics.Courtesy Armando Fraire MD. 32649b code lung pulmonary alveoli alveolus secondary lobule interlobular septa vein lymphatic histology interstitium interstitial |
|
Secondary Lobule and Interlobular Septa Kerley B line |
| 44194b01 81F hx atrial fibrillation cardiac failure heart failure CHF RA enlarged LA enlarged ground glass mosaic perfusion Kerley B lines varicose pulmonary veins squiggly sign Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
|
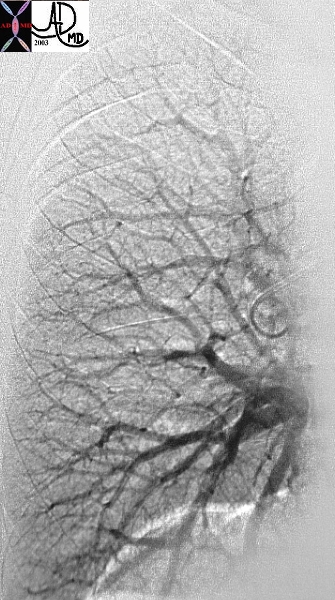
Venous Phase of the Pulmonary Angiogram Showing the Venous System |
| This is a normal venous phase of a digital pulmonary angiogram with arborization of the vessels almost from the venules to the upper vertically oriented veins and the lower horizontally oriented veins. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD. |
|
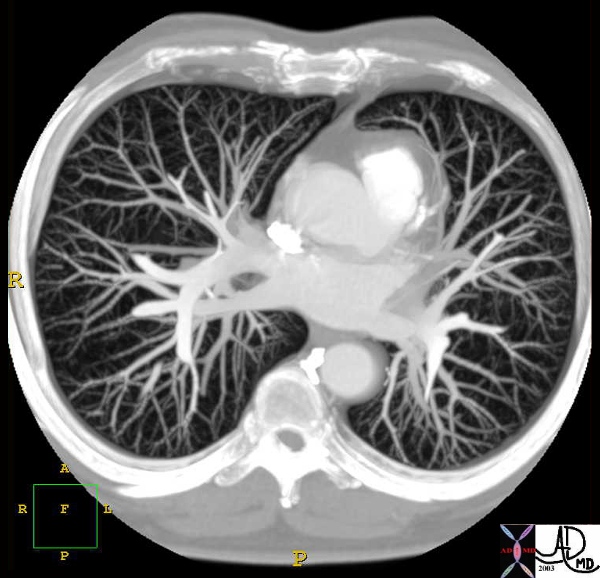
CTscan with both Venous and Arterial Phases |
| This compounded CT of the chest shows the pulmonary vascular circulation including the the pulmonary veins draining into the left atrium. The pulmonary arteries can be seen in the background. Courtesy Philips Medical Systems 32653 code chest lung pulmonary vein LA RVOT infundibulum normal anatomy radiology imaging CTscan |
|
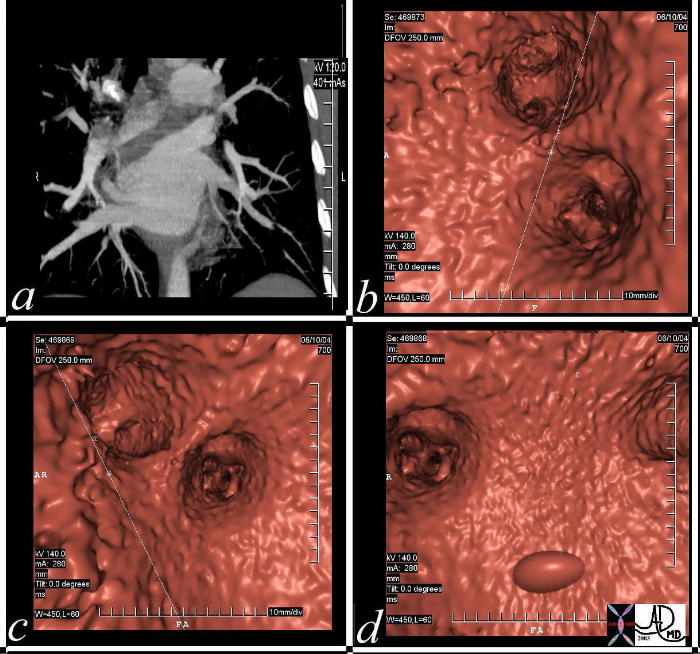
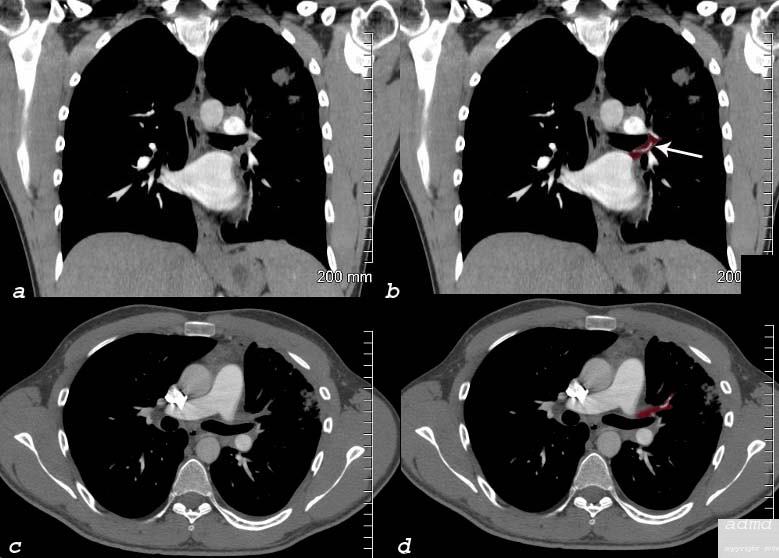
Virtual Study Showing Entry of Pulmonary Veins into the LA |
| This series of MDCT demonstrates the pulmonary veins and the left atrium in coronal projection (a) , and using virtual projections (b,c,d). Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 37236C code CVS heart cardiac left atrium LA pulmonary vein virtual MDCT imaging radiology CTscan virtual CTscan |
Applied Anatomy
|
Scimitar Syndrome Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return to the IVC |
| 01714c03 Copyright 2009 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
|
AVM from hepatopulmonary Syndrome |
| 24131 Copyright 2009 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
|
A?P Embolization of AVM |
| 24137 Copyright 2009 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
|
Thrombosed Left Upper Pulmonary Vein and Secondary Hemorrhage |
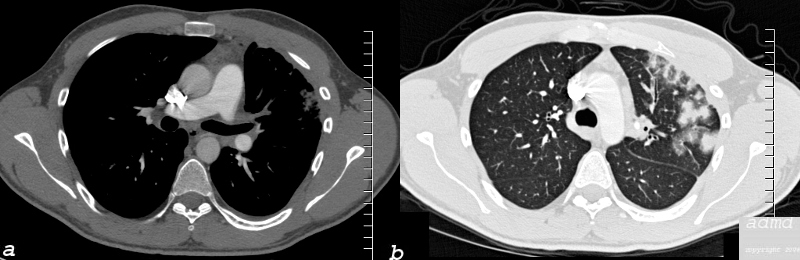
| 26 year old male who presents with shortness of breath a few months following RFA ablation for atrial fibrillation. Image a shows the left upper lobe thrombosed and the left lower vein contrast filled
Image b (the lung windows) shows thickening of the interlobular septa and secondary lobules distended with material, probably representing blood.
following male SOB s/p RFA ablation for atrial fibrillation lung pulmonary let upper lobe pulmonary vein thrombosed secondary lobule interlobular septa are thickened secondary lobule destroyed dx pulmonary vein thrombosis secondary to radiofrequency ablation therapy iatrogenic CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Scott Tsai MD ground glass changes pulmonary infarction venous infarction 75413c01 |
|
|
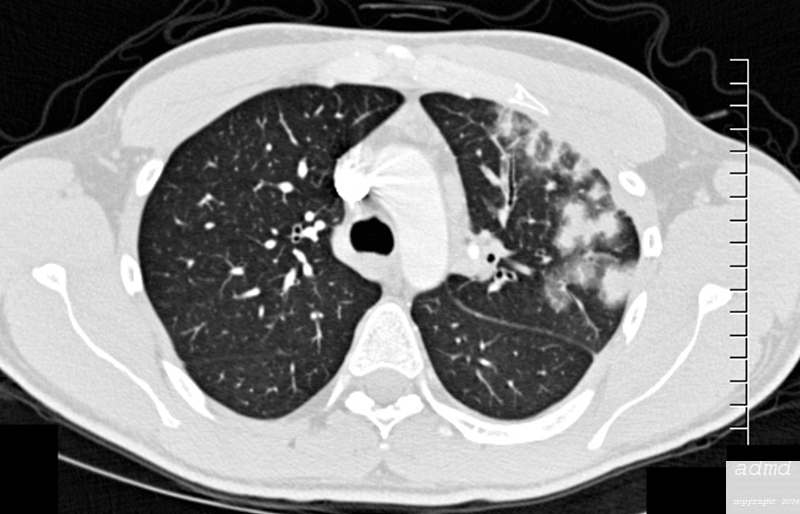
| 75413b01 26 male SOB s/p RFA ablation for atrial fibrillation lung pulmonary let upper lobe pulmonary vein thrombosed secondary lobule interlobular septa are thickened secondary lobule destroyed dx pulmonary vein thrombosis secondary to radiofrequency ablation therapy iatrogenic CT scan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Scott Tsai MD ground glass changes pulmonary infarction venous infarction |
|
|
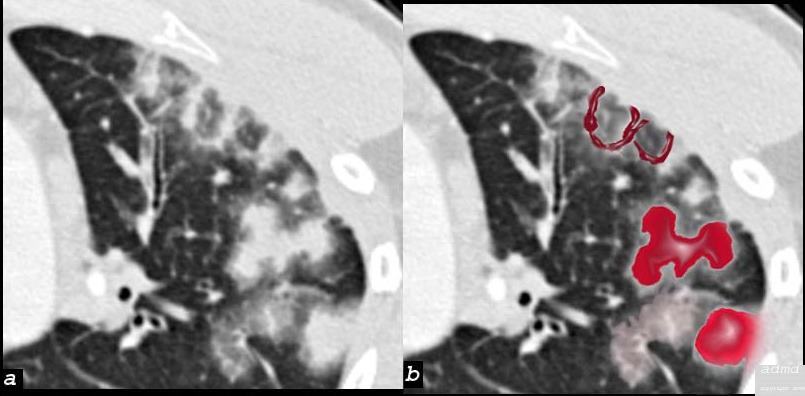
| 75413c07 26 male SOB s/p RFA ablation for atrial fibrillation lung pulmonary let upper lobe pulmonary vein thrombosed secondary lobule interlobular septa are thickened secondary lobule destroyed dx pulmonary vein thrombosis secondary to radiofrequency ablation therapy iatrogenic CT scan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Scott Tsai MD ground glass changes pulmonary infarction venous infarction |
|
Thrombosed left Upper Lobe Vein in Coronal and Sagittal View |
| 75413c08 26 male SOB s/p RFA ablation for atrial fibrillation lung pulmonary let upper lobe pulmonary vein thrombosed dx pulmonary vein thrombosis secondary to radiofrequency ablation therapy iatrogenic CT scan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Scott Tsai MD pulmonary infarction venous infarction |
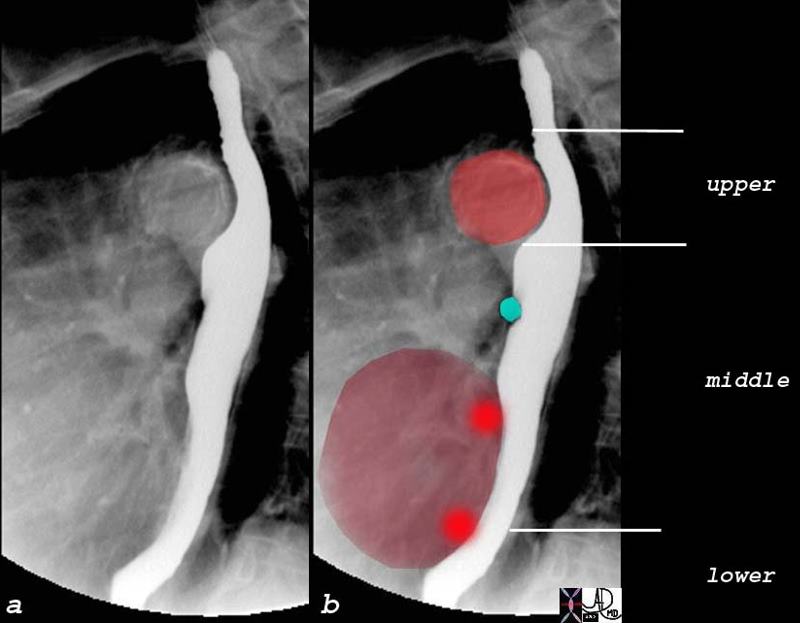
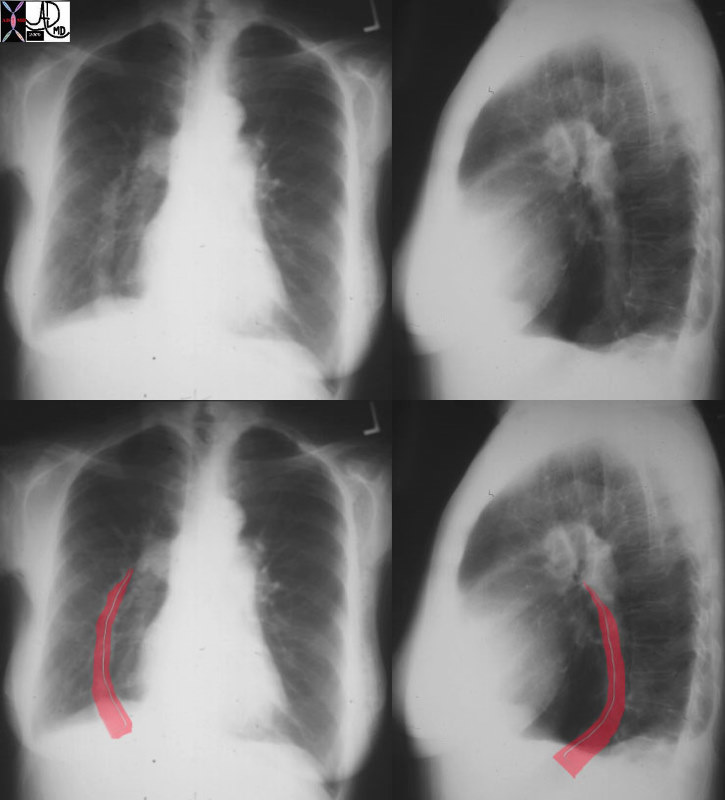
Relationship of the Left Sided Pulmonary Veins to the Esophagus |
| The normal indentations on the esophagus include the aortic arch and knob seen in bright red in b. The left bronchus is usually seen as a oblique line crossing the back of the esophagus, but in this case is seen as a focal indentation on the anterior wall. The left atrium is seen pulsating against the distal esophagus (maroon) usually when the left atrium is enlarged.
Copyright 2009 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 76119c02 |
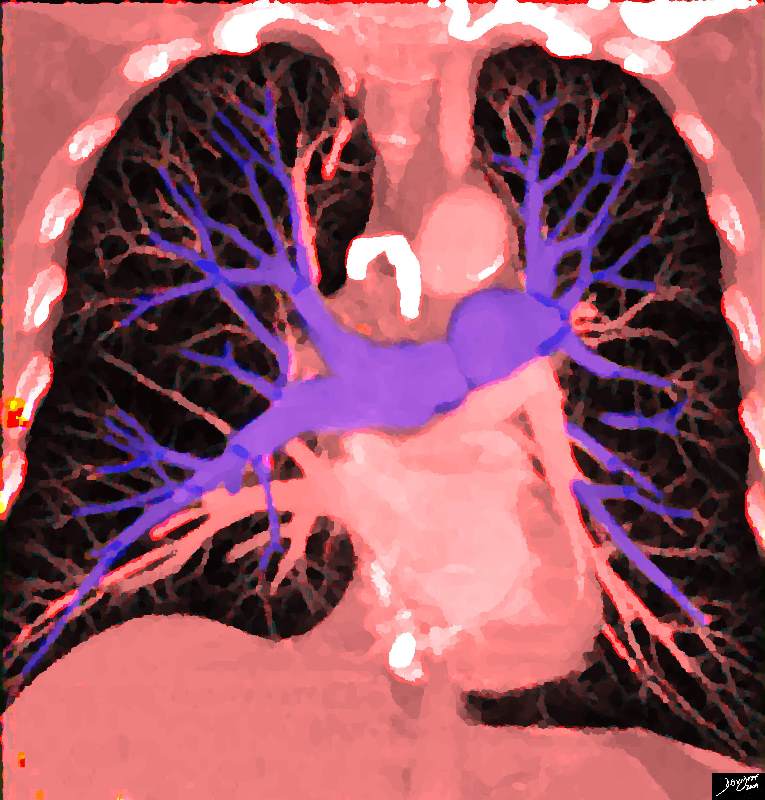
Pulmonary Circulation |
| 32807b03.8s heart cardiac pulmonary circulation pulmonary artery pulmonary vein left atrium Davidoff art copyright 2009 |
< prev next >