- Start with the Principles
- Know the Anatomy
- What is the RA
- parts/size/shape/position/character/time/connected to
- Most unique
- SVC and IVC and coronary sinus
- Most unique
- parts/size/shape/position/character/time/connected to

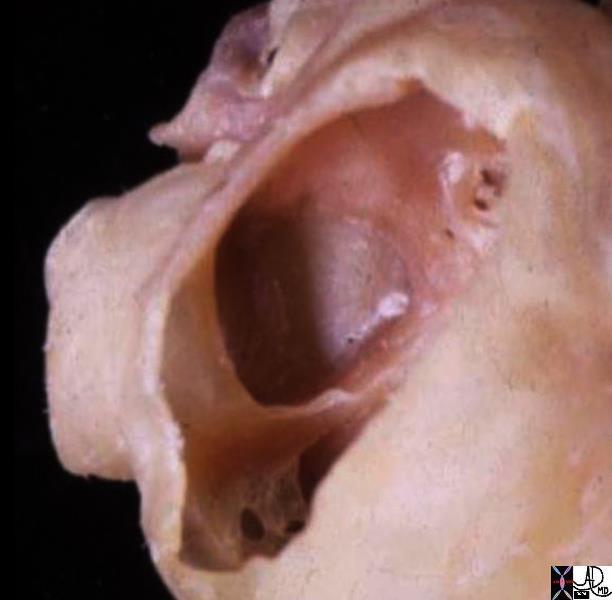
Thebesian Valves
The anterior wall has been removed In this waxed specimen created after distending the heart, allowing a window into the right atrial cavity and a focus on the fenestrated Thebesian valve which marks the entrance of the coronary sinus into the right atrium. The coronary sinus entrance lies just anterior and inferior to the Eustachian valve and the IVC, and just posterior to the tricuspid apparatus. right atrial appendage = RAA
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff TheCommonVein.net
06412cc02.81s
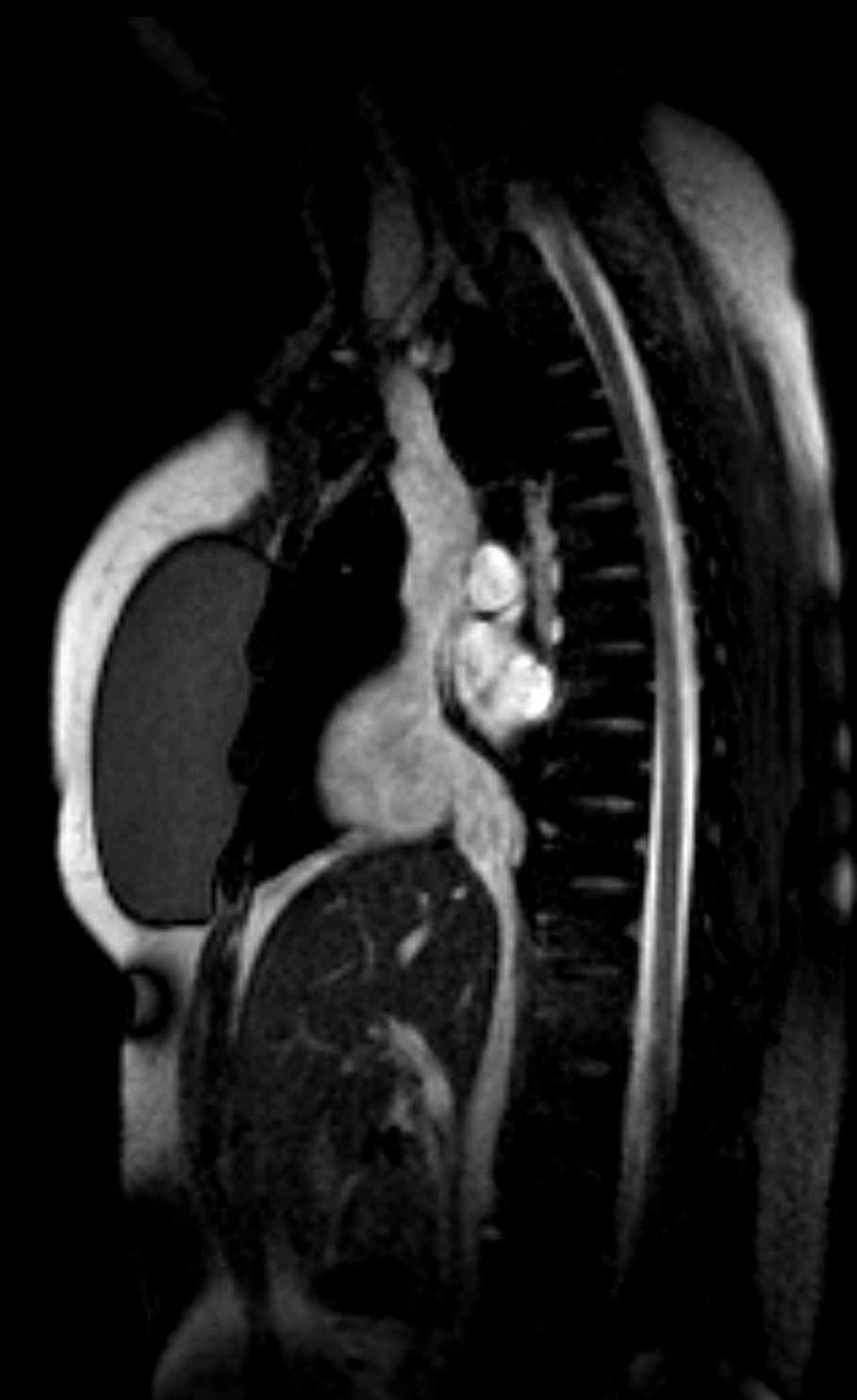
In this anatomic specimen the SVC and IVC are well seen and their lateral relationship to the right atrium is appreciated. They are embryological remnants of the sinus venosus and their similarity and conjoined structural origin and functionality can be well appreciated in this image. Davidoff MD
Key Words
heart cardiac RA right atrium thebesian valves coronary sinus Eustachian valve sulcus terminalis fossa ovalis foramen ovale septum secundum superior limbic band IVC inferior vena cava anatomy normal gross anatomy post mortem specimen
Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 2019 01707.6
Right Ventricle
parts/size/shape/position/character/time/connected to
Most unique
papillary muscles attached to the septum
trabeculations
Anterolateral and Posteromedial Papillary Septal Anterolateral Muscles of the Right Ventricle attached to the Ventricular Septum
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
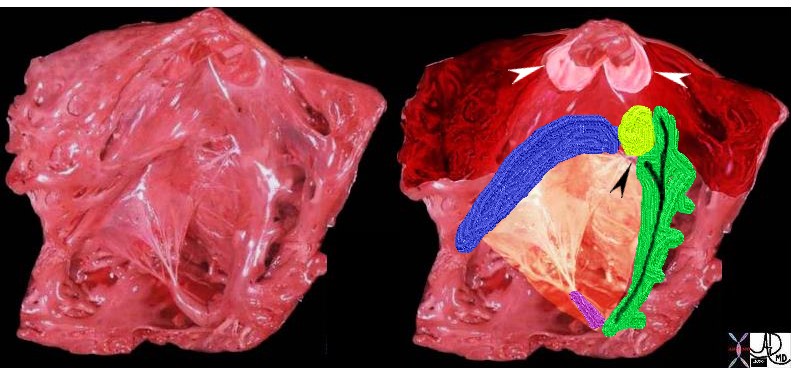
The superior aspect of the septal band (green in right image) has two limbs – the “Y” of the septal band. and the conal septum (lime green) embeds itself in the Y of the septal band. The (chordae) of the conal papillary muscle(aka papillary muscle of Lancisi- black arrow) also inserts in the “Y ” of the septal band. The anterolateral papillary muscle (purple )originates from the septal band) amd subtends the anterior leaflet of the tricuspid valve . The moderator band (not shown) connects the septum top the the free wall, and the parietal band (blue) completes the muscular ring that separates the inflow from the outflow tract. The pulmonary valve (white arrows) define the border between the RVOT and conus with the pulmonary artery.
Ashley Davidoff MD
06409c02
Courtesy of: Ashley Davidoff, MD
aka 37758b01c01.8s
aka heart anatomy P 040
Left Atrium
parts/size/shape/position/character/time/connected to
Most unique
U shaped septum primum
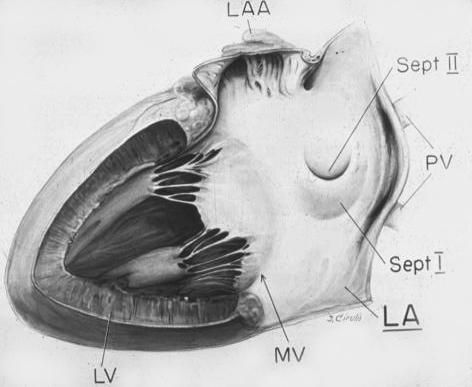
Courtesy Van Praagh and Van Praagh
Ashley Davidoff
Davidoff art copyright 2008 all rights reserved
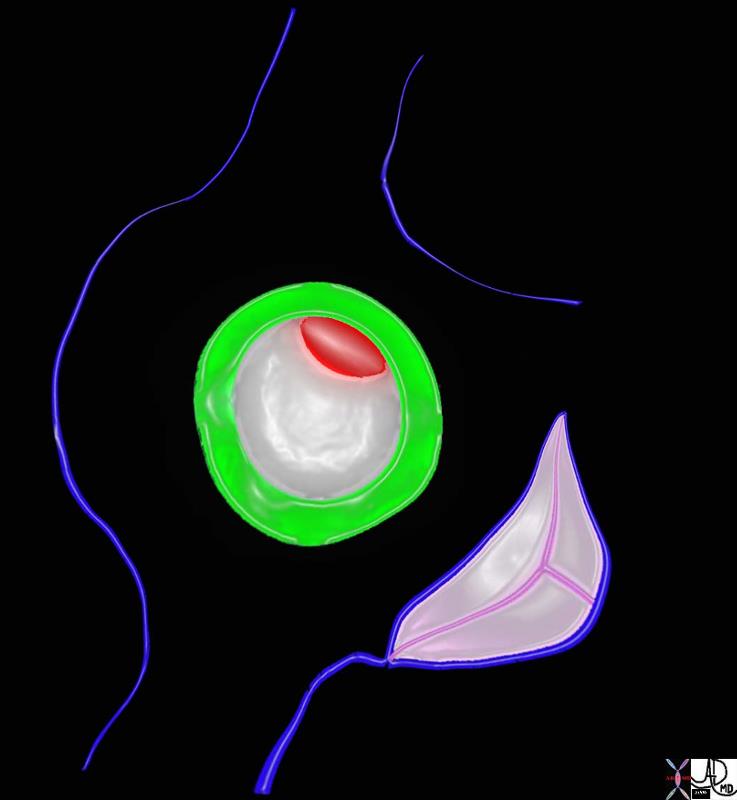
The green rim is septum secundum with the superior aspect called superior limbic band and the inferior aspect called the inferior limbic band. The white membrane is called the septum secundum, the superior aspect of which is the foramen ovale which in general closes over in later years.
key words
heart cardiac interatrial septum fossa ovalis foramen ovale superior limbic band inferior limbic band septum secundum septum primum tricuspid valve patent foramen ovale Davidoff art Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD
Left Ventricle
parts/size/shape/position/character/time/connected to
Most unique
papillary muscles NOT attached to the septum
smaller trabeculations
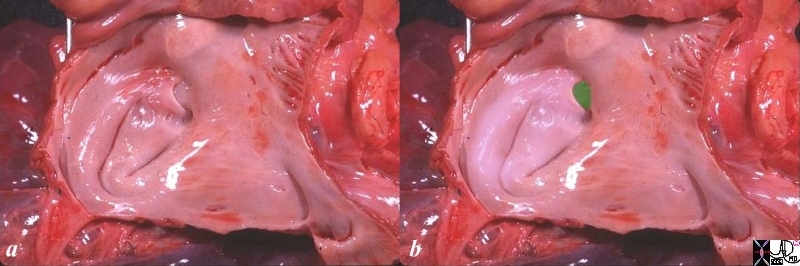
Anterolateral and Posteromedial Papillary Muscles of the Left Ventricle neither of which is attached to the Ventricular Septum
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net
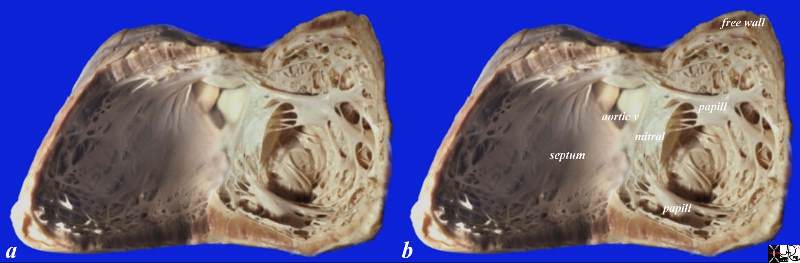
This normal anatomical specimen has been sectioned in long axis along the ventricular septum; then opened like a book with the septal wall seen on the left side of the image, and the free wall with the pair of papillary muscles seen on the right of the image. Note the fibrous continuity of the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve with the cusps of the aortic valve..
code 15389c05.8s Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2009
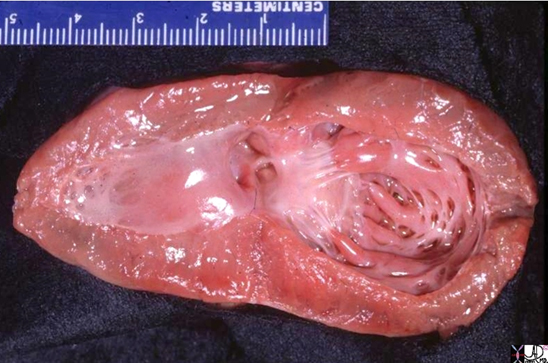
Ashley Davidoff MD

key words right atrium heart cardiac RA tricuspid valve TV left atrium LA MV mitralvalve RV right ventricle anterolateral papillary muscle interventricular septum left ventricle LV CTscan
Ashley Davidoff MD
34780
Aorta
parts/size/shape/position/character/time/connected to
Most unique
Brachiocephalic vessels arise from the aorta and never arise from the pulmonary artery


-
- Where is the Right Atrium?
-
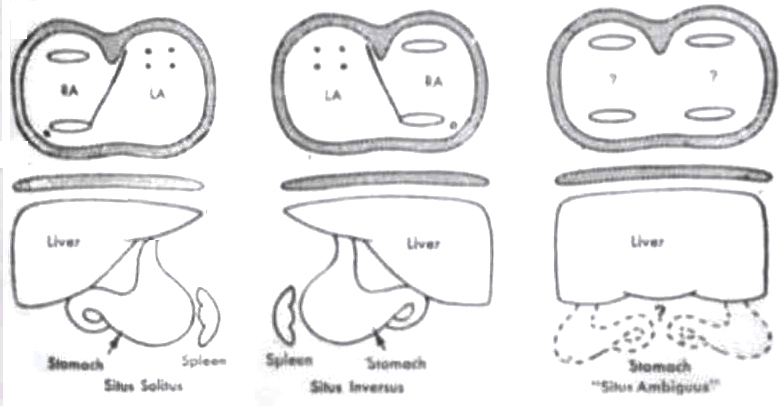
Situs Solitus Situs Inversus and Situs Ambiguus
Segmental Approach to Congenital heart Disease
Courtesy Van Praagh and van Praagh
TheCommonVein.net
keywords # liver stomach heart left atrium right atrium- Where is the Right ventricle? (D or L)
-
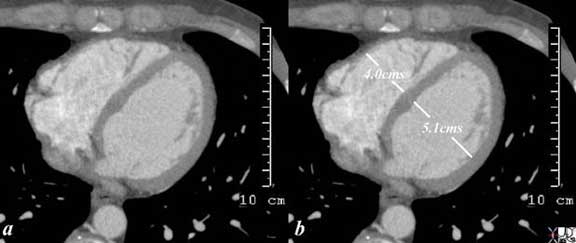
Normal size of the ventricular Walls in Diastole
Ashley Davidoff MD
TheCommonVein.net- Where is the Aorta? (D or L)
-
- S,D,D / S,L,L/ I,D,D / I,L,L/ A,D,D/A,L,L
-
- Are they Connected correctly?
- Where is the Aorta? (D or L)
PAPVR/TAVR/TOF/TGA/DORV/Truncus/DOLV
-
- Associated Anomalies?
VSD ASD PS AS Atresia Hypoplasia