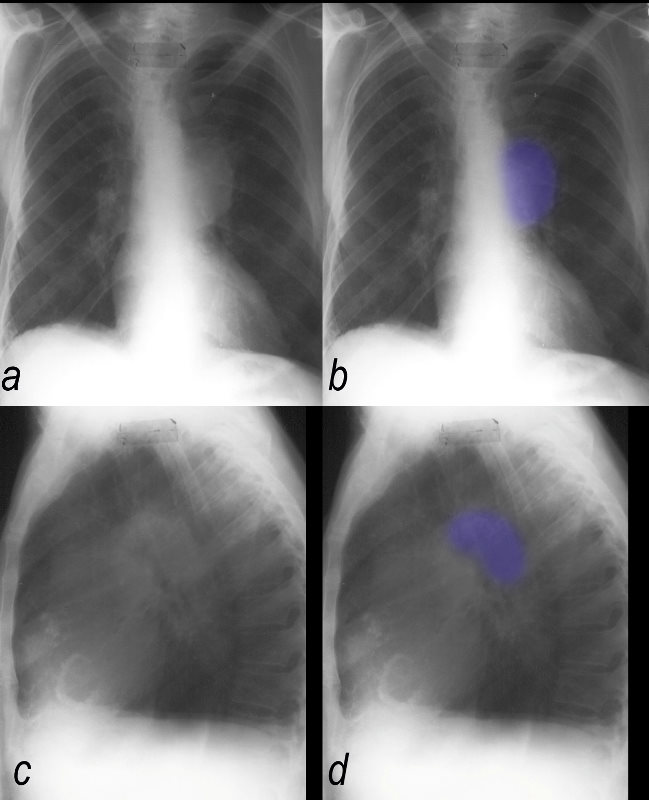
Tricuspid Annulus Calcification
60-year-old man with heart murmur since his teens, but recently became symptomatic with signs of right heart failure characterized ankle edema, ascites and anasarca. Examination confirmed massive ascites and peripheral edema with RV hypertrophy and a coarse ejection systolic murmur in the pulmonic area and absent second heart sound (pulmonic valve closure)
CXR shows aneurysmal dilatation of the left pulmonary artery, decrease pulmonary vasculature, and calcification of the pulmonary valve, pulmonary annulus and tricuspid valve annulus. EKG showed RVH
At catheterization there was a 100 mm Hg gradient across the valve, mean right atrial pressure was 16 mmHg, RV systolic pressure was 120/24 mmHg and PA pressure 25/12 mmHg. Femoral artery O2 sat was 87.5%
Ashley Davidoff MD
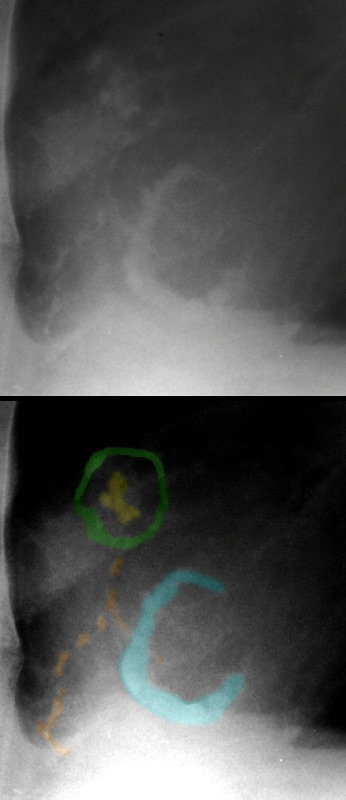
The pulmonary valve is nodular and calcified (yellow) surrounded by a calcified pulmonary annulus (green), associated with a calcified tricuspid annulus (teal), and scattered calcification over or in the right ventricle (orange).
Ashley Davidoff MD
References and Links
Sherif HM Calcification of left-sided valvular structures: evidence of a pro-inflammatory milieu. J Heart Valve Dis. 2009 Jan;18(1):52-60.